New method for long-term monitoring of intragastric pH
- PMID: 18081231
- PMCID: PMC4205461
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i47.6410
New method for long-term monitoring of intragastric pH
Abstract
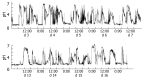
Aim: Consecutive monitoring of intragastric pH using the Bravo capsule.
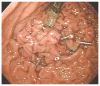
Methods: We put threads through a Bravo capsule and then affixed it to the gastric wall by endoscopic hemoclipping in seven subjects. Study data were uploaded to a computer via Datalink every 48 h. In this way, repeated monitoring of intragastric pH was undertaken.
Results: All subjects were able to monitor gastric pH over a 1-wk period, and five for > 2 wk. No complications were encountered during the monitoring. After pH monitoring, we safely retrieved the capsule endoscopically.
Conclusion: Clipping a Bravo capsule onto the gastric wall enabled long-term intragastric pH monitoring. This is a methodological report of pH monitoring over a period of > 2 wk.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bravo capsule system optimizes intragastric pH monitoring over prolonged time: effects of ghrelin on gastric acid and hormone secretion in the rat.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Oct 28;14(40):6180-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6180. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18985808 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate acid-suppressing effects of ranitidine hydrochloride and rabeprazole sodium following initial administration and reintroduction: A randomized, cross-over study using wireless pH monitoring capsules.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Apr;24(4):639-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05644.x. Epub 2008 Nov 20. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19032447 Clinical Trial.
-
Bravo capsule placement in the gastric cardia: a novel method for analysis of proximal stomach acid environment.Am J Gastroenterol. 2005 Aug;100(8):1721-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41733.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16086707
-
24-h recording of intragastric pH: technical aspects and clinical relevance.Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1999;230:9-16. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1999. PMID: 10499456 Review.
-
[New approaches to gastric ph-metry].Klin Med (Mosk). 2005;83(11):65-9. Klin Med (Mosk). 2005. PMID: 16404944 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
A novel placement method of a calibration-free pH capsule for continuous wireless measurement of intragastric pH in horses.J Vet Intern Med. 2025 Jan-Feb;39(1):e17273. doi: 10.1111/jvim.17273. J Vet Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39715411 Free PMC article.
-
A novel placement method of the Bravo wireless pH monitoring capsule for measuring intragastric pH.Dig Dis Sci. 2009 Mar;54(3):578-85. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0399-3. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Dig Dis Sci. 2009. PMID: 18649136
-
Evaluation of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Using the Bravo Capsule pH System.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Jan 31;22(1):25-30. doi: 10.5056/jnm15151. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016. PMID: 26717929 Free PMC article.
-
Wireless pH-metry at the gastrojejunostomy after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a novel use of the BRAVO™ system.Surg Endosc. 2011 Jul;25(7):2302-7. doi: 10.1007/s00464-010-1553-5. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Surg Endosc. 2011. PMID: 21298531
-
Large Buffering Effect of the Duodenal Bulb in Duodenal Switch: a Wireless pH-Metric Study.Obes Surg. 2017 Jul;27(7):1867-1871. doi: 10.1007/s11695-017-2574-0. Obes Surg. 2017. PMID: 28176219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Remes-Troche JM, Ibarra-Palomino J, Carmona-Sánchez RI, Valdovinos MA. Performance, tolerability, and symptoms related to prolonged pH monitoring using the Bravo system in Mexico. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:2382–2386. - PubMed
-
- Pandolfino JE, Richter JE, Ours T, Guardino JM, Chapman J, Kahrilas PJ. Ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring using a wireless system. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:740–749. - PubMed
-
- Gillies RS, Stratford JM, Booth MI, Dehn TC. Oesophageal pH monitoring using the Bravo catheter-free radio capsule. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;19:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Pandolfino JE, Schreiner MA, Lee TJ, Zhang Q, Boniquit C, Kahrilas PJ. Comparison of the Bravo wireless and Digitrapper catheter-based pH monitoring systems for measuring esophageal acid exposure. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:1466–1476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

