Translational mini-review series on complement factor H: structural and functional correlations for factor H
- PMID: 18081691
- PMCID: PMC2276926
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03553.x
Translational mini-review series on complement factor H: structural and functional correlations for factor H
Abstract
The 155-kDa glycoprotein, complement factor H (CFH), is a regulator of complement activation that is abundant in human plasma. Three-dimensional structures of over half the 20 complement control protein (CCP) modules in CFH have been solved in the context of single-, double- and triple-module segments. Proven binding sites for C3b occupy the N and C termini of this elongated molecule and may be brought together by a bend in CFH mediated by its central CCP modules. The C-terminal CCP 20 is key to the ability of the molecule to adhere to polyanionic markers on self-surfaces where CFH acts to regulate amplification of the alternative pathway of complement. The surface patch on CCP 20 that binds to model glycosaminoglycans has been mapped using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), as has a second glycosaminoglycan-binding patch on CCP 7. These patches include many of the residue positions at which sequence variations have been linked to three complement-mediated disorders: dense deposit disease, age-related macular degeneration and atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome. In one plausible model, CCP 20 anchors CFH to self-surfaces via a C3b/polyanion composite binding site, CCP 7 acts as a 'proof-reader' to help discriminate self- from non-self patterns of sulphation, and CCPs 1-4 disrupt C3/C5 convertase formation and stability.
Figures

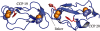


References
-
- Mold C, Gewurz H, Du Clos TW. Regulation of complement activation by C-reactive protein. Immunopharmacology. 1999;42:23–30. - PubMed
-
- Sjoberg A, Onnerfjord P, Morgelin M, Heinegard D, Blom AM. The extracellular matrix and inflammation: fibromodulin activates the classical pathway of complement by directly binding C1q. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:32301–8. - PubMed
-
- Pio R, Martinez A, Unsworth EJ, et al. Complement factor H is a serum-binding protein for adrenomedullin, and the resulting complex modulates the bioactivities of both partners. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:12292–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

