Mucin immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis and mapping of extramammary Paget's disease
- PMID: 18081697
- PMCID: PMC3918076
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00188.x
Mucin immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis and mapping of extramammary Paget's disease
Abstract
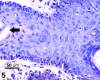
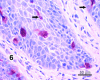
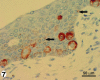
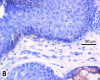
Extramammary Paget's disease (EMPD) is a rare skin cancer of the genital region in which cancer cells with enlarged nuclei and pale cytoplasm are scattered singly in the affected epidermis. These cancer cells, called Paget cells, contain mucin, which is never found in normal epidermis. The oligosaccharide side chains of Paget cell mucin end with sialic acid. Sialic acid is easily detected by zirconyl haematoxylin or alcian blue. The other sugars in the oligosaccharide chains can be detected by the periodic acid-Shiff reaction. Rarely, the diagnosis of EMPD is complicated by the absence of mucin from the Paget cells. We have examined such an atypical case. The oligosaccharide side chains, including the sialic acids, are absent. In both this case and a typical case, the Paget cells contain epithelial membrane antigen mucin (MUC1) core protein and usually contain gastric surface-type mucin (MUC5AC) core protein, which can be stained by antibodies. Since neither core protein is found in normal epidermis, epithelial membrane antigen core protein may be the most reliable diagnostic marker for extramammary Paget's disease. In both the atypical case and the typical case of Paget's disease, some cells that look like keratinocytes contain mucin core proteins. These may be incipient Paget cells. We suggest that using th epithelial membrane antigen core protein as a marker for the true extent of extramammary Paget's disease could facilitate complete excision and reduce the rate of recurrence.
Figures
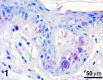
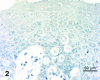
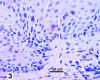
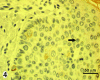
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of mucin genes in mammary and extramammary Paget's disease.Am J Surg Pathol. 2001 Dec;25(12):1469-77. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200112000-00001. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11717535
-
Zirconyl hematoxylin vs. alcian blue staining in a case of extramammary Paget's disease.J Cutan Pathol. 2003 Jul;30(6):401-4. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0560.2003.00080.x. J Cutan Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12834490
-
Evidence from mucin core protein expression that some Paget's disease on areola can be of extramammary-like histogenesis and part of multisite disease.Br J Dermatol. 2004 Sep;151(3):688-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06087.x. Br J Dermatol. 2004. PMID: 15377360
-
Ectopic extramammary Paget's disease: case report and literature review.Acta Derm Venereol. 2010 Sep;90(5):502-5. doi: 10.2340/00015555-0892. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010. PMID: 20814627 Review.
-
Mammary and extramammary Paget's disease.J Clin Pathol. 2000 Oct;53(10):742-9. doi: 10.1136/jcp.53.10.742. J Clin Pathol. 2000. PMID: 11064666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling and Structural Characterization of High Neu5Gc or Sulfate-containing O-glycans from Hyla Rabbit Intestinal Mucin.Molecules. 2019 Apr 7;24(7):1365. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071365. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30959980 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease Combined with Bowen's Disease in Vulva.Ann Dermatol. 2011 Oct;23(Suppl 2):S222-5. doi: 10.5021/ad.2011.23.S2.S222. Epub 2011 Oct 31. Ann Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 22148056 Free PMC article.
-
Muc5ac mucin expression during rat skin development.Eur J Histochem. 2015 Feb 20;59(1):2462. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2015.2462. Eur J Histochem. 2015. PMID: 25820562 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-Paget cells: Evidence of keratinocyte origin of extramammary Paget's disease.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2019 Aug;8(3):203-205. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2019.01096. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2019. PMID: 31523599 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Extramammary Paget Disease by Two-Photon Microscopy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 25;9:839786. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.839786. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35280872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eller JJ, Eller WD. Tumors of the Skin. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1951.
-
- Jones RE, Austin C, Ackerman AB. Extramammary Paget's disease: a critical reexamination. Am J Dermatopathol. 1979;1:101–32. - PubMed
-
- Sasai Y, Nakama T, Kasuda M. Sialomucin in Paget cells of extrammary Paget's disease. Histochem J. 1983;15:987–97. - PubMed
-
- Kondo Y, Kashima K, Daa T, Fujiwara S, Nakayama I, Yokoyama Y. The ectopic expression of gastric mucin in extramam-mary and mammary Paget's disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:617–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

