Expression of the NF-kappaB inhibitor ABIN-3 in response to TNF and toll-like receptor 4 stimulation is itself regulated by NF-kappaB
- PMID: 18081698
- PMCID: PMC3823492
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00187.x
Expression of the NF-kappaB inhibitor ABIN-3 in response to TNF and toll-like receptor 4 stimulation is itself regulated by NF-kappaB
Abstract
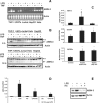
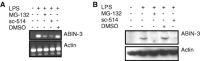
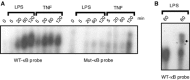
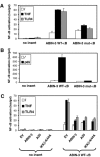
Although the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB)-dependent gene expression is critical to the induction of an efficient immune response to infection or tissue injury, excessive or prolonged NF-kappaB signalling can contribute to the development of several inflammatory diseases. Therefore, the NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway is tightly regulated by several intracellular proteins. We have previously identified A20-binding inhibitor of NF-kappaB activation (ABIN)-3 as an lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-inducible protein in monocytes that negatively regulates NF-B activation in response to tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and LPS. Here we report that ABIN-3 expression is also up-regulated upon TNF treatment of monocytes and other non-myeloid cell types. We also found a significantly enhanced expression of ABIN-3 in monocytes of sepsis patients, which is restored to control levels by corticotherapy. To further understand the transcriptional regulation of ABIN-3 expression, we isolated the human ABIN-3 promoter and investigated its activation in response to TNF and LPS. This revealed that the LPS- and TNF-inducible expression of ABIN-3 is dependent on the binding of NF-kappaB to a specific B site in the ABIN-3 promoter. Altogether, these data indicate an important role for NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression of ABIN-3 in the negative feedback regulation of TNF receptor and toll-like receptor 4 induced NF-kappaB activation.
Figures


References
-
- Gilmore TD. Introduction to NF-kappaB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene. 2006;25:6680–4. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann A, Natoli G, Gosh G. Transcriptional regulation via the NF-kappaB signaling module. Oncogene. 2006;25:6706–16. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Takada Y, Boriek AM, Aggarwal BB. Nuclear factor-kappaB: its role in health and disease. J Mol Med. 2004;82:434–48. - PubMed
-
- Lang T, Mansell A. The negative regulation of Toll-like receptor and associated pathways. Immunol Cell Biol. 2007;85:425–34. - PubMed
-
- Wullaert A, Heyninck K, Janssens S, Beyaert R. Ubiquitin: tool and target for intracellular NF-kappaB inhibitors. Trends Immunol. 2006;27:533–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

