Effects of urinary incontinence, comorbidity and race on quality of life outcomes in women
- PMID: 18082212
- PMCID: PMC2671469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.09.074
Effects of urinary incontinence, comorbidity and race on quality of life outcomes in women
Abstract
Purpose: We investigated the effects of comorbidity and urinary incontinence on both generic and incontinence specific quality of life outcome measures, and investigated whether the association between urinary incontinence and quality of life varies by race.
Materials and methods: Study participants were 2,109 women 40 to 69 years old randomly selected from an urban health maintenance organization and interviewed in person for a study of risk factors for urinary incontinence. The sample was racially diverse consisting of 48% white, 18% black, 17% Hispanic and 16% Asian-American women. In addition to incontinence, reproductive and medical history questionnaires, all participants completed the Medical Outcomes Study Short Form 36, a measure of health related quality of life. All participants with daily and weekly incontinence (29%) completed the Incontinence Impact Questionnaire, an incontinence specific quality of life measure. The health maintenance organization's inpatient and outpatient electronic databases were used to calculate a Charlson comorbidity index score for each participant. ANCOVA was used to produce a model adjusting for sociodemographic variables, comorbidity and incontinence frequency. The same model was run for each of 4 racial groupings to examine differences by race/ethnicity.
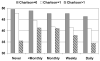
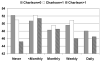
Results: Urinary incontinence is significantly associated with a decreased quality of life and those with more frequent incontinence have significantly lower quality of life scores. In our model the Charlson score, an objective measure of comorbidity based on hospital and physician records, also has a significant negative impact on quality of life. When comorbidity is controlled, incontinence frequency continues to have a significant negative association with quality of life except among the sickest women. For women with the greatest extent of comorbidity, incontinence frequency is not significantly associated with negative quality of life outcomes. We did not find clear patterns of variation by race.
Conclusions: Urinary incontinence and comorbidity each have an independent and significant role in reducing quality of life outcomes for all but the sickest women.
Figures



References
-
- Van Oyen H, Van Oyen P. Urinary incontinence in Belgium; prevalence, correlates and psychosocial consequences. Acta Clin Belg. 2002 Jul;57(4):207–18. - PubMed
-
- Ware JE, Snow K, Kosinski M, Gandek B. SF-36 Health Survey Manual and Interpretation Guide. Boston, Massachusetts: The Health Institute; 1993.
-
- Fultz NH, Herzog AR. Self-reported social and emotional impact of urinary incontinence. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001 Jul;49(7):892–9. - PubMed
-
- Lagro-Janssen T, Smits A, Van Weel C. Urinary incontinence in women and the effects on their lives. Scand J Prim Health Care. 1992 Sep;10(3):211–6. - PubMed
-
- Fultz NH, Fisher GG, Jenkins KR. Does urinary incontinence affect middle-aged and older women’s time use and activity patterns? Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Dec;104(6):1327–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

