Coordinated control of dCTCF and gypsy chromatin insulators in Drosophila
- PMID: 18082602
- PMCID: PMC2579779
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.024
Coordinated control of dCTCF and gypsy chromatin insulators in Drosophila
Abstract
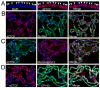
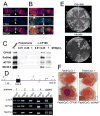
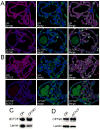
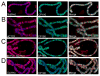
CTCF plays a central role in vertebrate insulators and forms part of the Fab-8 insulator in Drosophila. dCTCF is present at hundreds of sites in the Drosophila genome, where it is located at the boundaries between bands and interbands in polytene chromosomes. dCTCF colocalizes with CP190, which is required for proper binding of dCTCF to chromatin, but not with the other gypsy insulator proteins Su(Hw) or Mod(mdg4)2.2. Mutations in the CP190 gene affect Fab-8 insulator activity, suggesting that CP190 is an essential component of both gypsy and dCTCF insulators. dCTCF is present at specific nuclear locations, forming large insulator bodies that overlap with those formed by Su(Hw), Mod(mdg4)2.2, and CP190. The results suggest that Su(Hw) and dCTCF may be the DNA-binding components of two different subsets of insulators that share CP190 and cooperate in the formation of insulator bodies to regulate the organization of the chromatin fiber in the nucleus.
Figures


References
-
- Barges S, Mihaly J, Galloni M, Hagstrom K, Muller M, Shanower G, Schedl P, Gyurkovics H, Karch F. The Fab-8 boundary defines the distal limit of the bithorax complex iab- 7 domain and insulates iab-7 from initiation elements and a PRE in the adjacent iab-8 domain. Development. 2000;127:779–790. - PubMed
-
- Bell AC, Felsenfeld G. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature. 2000;405:482–485. - PubMed
-
- Bell AC, West AG, Felsenfeld G. The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell. 1999;98:387–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

