PHD domain-mediated E3 ligase activity directs intramolecular sumoylation of an adjacent bromodomain required for gene silencing
- PMID: 18082607
- PMCID: PMC4348069
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.11.012
PHD domain-mediated E3 ligase activity directs intramolecular sumoylation of an adjacent bromodomain required for gene silencing
Abstract
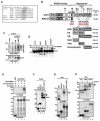
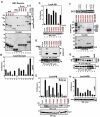
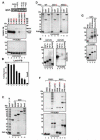
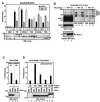
Tandem PHD and bromodomains are often found in chromatin-associated proteins and have been shown to cooperate in gene silencing. Each domain can bind specifically modified histones: the mechanisms of cooperation between these domains are unknown. We show that the PHD domain of the KAP1 corepressor functions as an intramolecular E3 ligase for sumoylation of the adjacent bromodomain. The RING finger-like structure of the PHD domain is required for both Ubc9 binding and sumoylation and directs modification to specific lysine residues in the bromodomain. Sumoylation is required for KAP1-mediated gene silencing and functions by directly recruiting the SETDB1 histone methyltransferase and the CHD3/Mi2 component of the NuRD complex via SUMO-interacting motifs. Sumoylated KAP1 stimulates the histone methyltransferase activity of SETDB1. These data provide a mechanistic explanation for the cooperation of PHD and bromodomains in gene regulation and describe a function of the PHD domain as an intramolecular E3 SUMO ligase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
It takes a PHD to SUMO.Trends Biochem Sci. 2008 May;33(5):191-4. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2008.02.003. Epub 2008 Apr 9. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008. PMID: 18406149
-
Epigenetic gene silencing by the SRY protein is mediated by a KRAB-O protein that recruits the KAP1 co-repressor machinery.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 18;284(51):35670-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.032086. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19850934 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into human KAP1 PHD finger-bromodomain and its role in gene silencing.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Jun;15(6):626-33. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1416. Epub 2008 May 18. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18488044 Free PMC article.
-
Immune regulation by the SUMO family.Nat Rev Immunol. 2025 Aug;25(8):608-620. doi: 10.1038/s41577-025-01155-4. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40108400 Review.
-
The SUMO Pathway.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2957:1-15. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4710-3_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40875111 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Kruppel-associated Box (KRAB)-associated Co-repressor KAP1 Ser-473 Phosphorylation in DNA Damage Response.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 1;287(23):18937-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.313262. Epub 2012 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22496453 Free PMC article.
-
Reading, writing, and repair: the role of ubiquitin and the ubiquitin-like proteins in DNA damage signaling and repair.Front Genet. 2013 Apr 1;4:45. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00045. eCollection 2013. Front Genet. 2013. PMID: 23554604 Free PMC article.
-
LMP1-Induced Sumoylation Influences the Maintenance of Epstein-Barr Virus Latency through KAP1.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7465-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00711-15. Epub 2015 May 6. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25948750 Free PMC article.
-
KRAB domain of ZFP568 disrupts TRIM28-mediated abnormal interactions in cancer cells.NAR Cancer. 2020 Jun;2(2):zcaa007. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcaa007. Epub 2020 May 18. NAR Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32743551 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated regulation of transcription factor Bcl11b activity in thymocytes by the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways and protein sumoylation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 3;287(32):26971-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.344176. Epub 2012 Jun 14. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22700985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boggio R, Colombo R, Hay RT, Draetta GF, Chiocca S. A mechanism for inhibiting the SUMO pathway. Mol Cell. 2004;16:549–561. - PubMed
-
- Bylebyl GR, Belichenko I, Johnson ES. The SUMO isopeptidase Ulp2 prevents accumulation of SUMO chains in yeast. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:44113–44120. - PubMed
-
- Friedman JR, Fredericks WJ, Jensen DE, Speicher DW, Huang XP, Neilson EG, Rauscher FJ., 3rd KAP-1, a novel corepressor for the highly conserved KRAB repression domain. Genes Dev. 1996;10:2067–2078. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 CA009173/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI041711/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI41136/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA09173/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA126283/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA87658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA092088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA095561/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R29 AI041711/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI41711/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009171/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI041136/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095561/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM57599/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI041136/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

