Integrin beta1-mediated matrix assembly and signaling are critical for the normal development and function of the kidney glomerulus
- PMID: 18082680
- PMCID: PMC3947521
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.10.047
Integrin beta1-mediated matrix assembly and signaling are critical for the normal development and function of the kidney glomerulus
Abstract
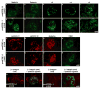
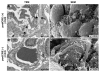
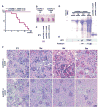
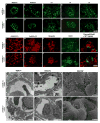
The human kidneys filter 180 l of blood every day via about 2.5 million glomeruli. The three layers of the glomerular filtration apparatus consist of fenestrated endothelium, specialized extracellular matrix known as the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) and the podocyte foot processes with their modified adherens junctions known as the slit diaphragm (SD). In this study we explored the contribution of podocyte beta1 integrin signaling for normal glomerular function. Mice with podocyte specific deletion of integrin beta1 (podocin-Cre beta1-fl/fl mice) are born normal but cannot complete postnatal renal development. They exhibit detectable proteinuria on day 1 and die within a week. The kidneys of podocin-Cre beta1-fl/fl mice exhibit normal glomerular endothelium but show severe GBM defects with multilaminations and splitting including podocyte foot process effacement. The integrin linked kinase (ILK) is a downstream mediator of integrin beta1 activity in epithelial cells. To further explore whether integrin beta1-mediated signaling facilitates proper glomerular filtration, we generated mice deficient of ILK in the podocytes (podocin-Cre ILK-fl/fl mice). These mice develop normally but exhibit postnatal proteinuria at birth and die within 15 weeks of age due to renal failure. Collectively, our studies demonstrate that podocyte beta1 integrin and ILK signaling is critical for postnatal development and function of the glomerular filtration apparatus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Podocyte-specific deletion of integrin-linked kinase results in severe glomerular basement membrane alterations and progressive glomerulosclerosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006 May;17(5):1334-44. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005090921. Epub 2006 Apr 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 16611717
-
Early glomerular filtration defect and severe renal disease in podocin-deficient mice.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jan;24(2):550-60. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.2.550-560.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14701729 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of integrin-linked kinase in podocyte biology: Bridging the integrin and slit diaphragm signaling.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006 Aug;17(8):2164-75. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006010033. Epub 2006 Jul 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 16837631
-
[Structure and function of the glomerular filtration barrier].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2005 Mar;18(105):317-20. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2005. PMID: 15997642 Review. Polish.
-
Regulation of adhesive interaction between podocytes and glomerular basement membrane.Microsc Res Tech. 2002 May 15;57(4):247-53. doi: 10.1002/jemt.10083. Microsc Res Tech. 2002. PMID: 12012393 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the podocyte (and glomerular endothelium) in building the GBM.Semin Nephrol. 2012 Jul;32(4):342-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.06.005. Semin Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22958488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ILK/PINCH/parvin complex: the kinase is dead, long live the pseudokinase!EMBO J. 2010 Jan 20;29(2):281-91. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.376. Epub 2009 Dec 24. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20033063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin-Linked Kinase Deficiency in Collecting Duct Principal Cell Promotes Necroptosis of Principal Cell and Contributes to Kidney Inflammation and Fibrosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Nov;30(11):2073-2090. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2018111162. Epub 2019 Oct 25. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31653783 Free PMC article.
-
Podocyte injury caused by indoxyl sulfate, a uremic toxin and aryl-hydrocarbon receptor ligand.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 22;9(9):e108448. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108448. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25244654 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoethanolamine methyltransferases in phosphocholine biosynthesis: functions and potential for antiparasite therapy.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011 Jul;35(4):609-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00267.x. Epub 2011 Mar 10. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21303393 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrahamson DR. Structure and development of the glomerular capillary wall and basement membrane. Am J Physiol. 1987;253:F783–94. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamson DR, Prettyman AC, Robert B, John PL. Laminin-1 reexpression in Alport mouse glomerular basement membranes. Kidney Int. 2003;63:826–34. - PubMed
-
- Aumailley M, Pesch M, Tunggal L, Gaill F, Fassler R. Altered synthesis of laminin 1 and absence of basement membrane component deposition in (beta)1 integrin-deficient embryoid bodies. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 2):259–68. - PubMed
-
- Baraldi A, Zambruno G, Furci L, Manca V, Vaschieri C, Lusvarghi E. Beta-1 integrins in the normal human glomerular capillary wall: an immunoelectron microscopy study. Nephron. 1994;66:295–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

