Acute induction of epileptiform discharges by pilocarpine in the in vitro isolated guinea-pig brain requires enhancement of blood-brain barrier permeability
- PMID: 18082973
- PMCID: PMC2774816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.10.037
Acute induction of epileptiform discharges by pilocarpine in the in vitro isolated guinea-pig brain requires enhancement of blood-brain barrier permeability
Abstract
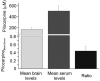
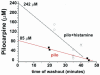
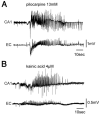
Systemic application of the muscarinic agonist, pilocarpine, is commonly utilized to induce an acute status epilepticus that evolves into a chronic epileptic condition characterized by spontaneous seizures. Recent findings suggest that the status epilepticus induced by pilocarpine may be triggered by changes in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability. We tested the role of the BBB in an acute pilocarpine model by using the in vitro model brain preparation and compared our finding with in vivo data. Arterial perfusion of the in vitro isolated guinea-pig brain with <1 mM pilocarpine did not cause epileptiform activity, but rather reduced synaptic transmission and induced steady fast (20-25 Hz) oscillatory activity in limbic cortices. These effects were reversibly blocked by co-perfusion of the muscarinic antagonist atropine sulfate (5 microM). Brain pilocarpine measurements in vivo and in vitro suggested modest BBB penetration. Pilocarpine induced epileptiform discharges only when perfused with compounds that enhance BBB permeability, such as bradykinin (n=2) or histamine (n=10). This pro-epileptic effect was abolished when the BBB-impermeable muscarinic antagonist atropine methyl bromide (5 microM) was co-perfused with histamine and pilocarpine. In the absence of BBB permeability enhancing drugs, pilocarpine induced epileptiform activity only after arterial perfusion at concentrations >10 mM. Ictal discharges correlated with a high intracerebral pilocarpine concentration measured by high pressure liquid chromatography. We propose that acute epileptiform discharges induced by pilocarpine treatment in the in vitro isolated brain preparation are mediated by a dose-dependent, atropine-sensitive muscarinic effect promoted by an increase in BBB permeability. Pilocarpine accumulation secondary to BBB permeability changes may contribute to in vivo ictogenesis in the pilocarpine epilepsy model.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ictal epileptiform activity in the CA3 region of hippocampal slices produced by pilocarpine.J Neurophysiol. 1998 Jun;79(6):3019-29. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.6.3019. J Neurophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9636105
-
In vivo and in vitro effects of pilocarpine: relevance to ictogenesis.Epilepsia. 2007 Oct;48(10):1934-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01185.x. Epub 2007 Jul 20. Epilepsia. 2007. PMID: 17645533 Free PMC article.
-
Propagation dynamics of epileptiform activity acutely induced by bicuculline in the hippocampal-parahippocampal region of the isolated Guinea pig brain.Epilepsia. 2005 Dec;46(12):1914-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.00342.x. Epilepsia. 2005. PMID: 16393157
-
The in vitro isolated whole guinea pig brain as a model to study epileptiform activity patterns.J Neurosci Methods. 2016 Feb 15;260:83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.03.026. Epub 2015 Apr 2. J Neurosci Methods. 2016. PMID: 25843067 Review.
-
Are you in or out? Leukocyte, ion, and neurotransmitter permeability across the epileptic blood-brain barrier.Epilepsia. 2012 Jun;53 Suppl 1(0 1):26-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03472.x. Epilepsia. 2012. PMID: 22612806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immature dentate gyrus: an endophenotype of neuropsychiatric disorders.Neural Plast. 2013;2013:318596. doi: 10.1155/2013/318596. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Neural Plast. 2013. PMID: 23840971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Regional Specific Alterations in BBB Permeability are Relevant to the Differential Responses of 67-kDa LR Expression in Endothelial Cells and Astrocytes Following Status Epilepticus.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 29;20(23):6025. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236025. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31795399 Free PMC article.
-
Does brain inflammation mediate pathological outcomes in epilepsy?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;813:169-83. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-8914-1_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25012376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Causes of CNS inflammation and potential targets for anticonvulsants.CNS Drugs. 2013 Aug;27(8):611-23. doi: 10.1007/s40263-013-0078-6. CNS Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23771734 Review.
-
Dual Targeting by Inhibition of Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Attenuates the Neuroinflammatory Responses in Murine Hippocampal Cells and Seizures in C57BL/6 Mice.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 23;12:739452. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.739452. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34887852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Rahman A, Shetty AK, Abou-Donia MB. Acute exposure to sarin increases blood brain barrier permeability and induces neuropathological changes in the rat brain: dose-response relationships. Neuroscience. 2002;113:721–741. - PubMed
-
- Arzt ES, Fernandez-Castelo S, Diaz A, Finkielman S, Nahmod VE. The muscarinic agonist pilocarpine inhibits DNA and inter-feron-gamma synthesis in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1989;11:275–281. - PubMed
-
- Biella G, de Curtis M. Olfactory inputs activate the medial entorhinal cortex via the hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 2000;83:1924–1931. - PubMed
-
- Biesold D, Inanami O, Sato A, Sato Y. Stimulation of the nucleus basalis of Meynert increases cerebral cortical blood flow in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1989;98:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Bregola G, Varani K, Gessi S, Beani L, Bianchi C, Borea PA, Regoli D, Simonato M. Changes in hippocampal and cortical B1 bradykinin receptor biological activity in two experimental models of epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1999;92:1043–1049. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

