Transcription factor broad suppresses precocious development of adult structures during larval-pupal metamorphosis in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum
- PMID: 18083350
- PMCID: PMC3556786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mod.2007.11.001
Transcription factor broad suppresses precocious development of adult structures during larval-pupal metamorphosis in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum
Abstract
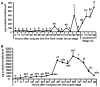
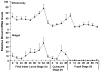
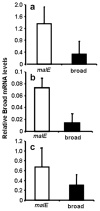
Broad (br), a transcription factor containing the Broad-Tramtrack-Bric-a-brac (BTB) and zinc finger domains was shown to mediate 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) action and pupal development in Drosophila melanogaster and Manduca sexta. We determined the key roles of br during larval-pupal metamorphosis using RNA interference (RNAi) in a coleopteran insect, Tribolium castaneum. Two major peaks of T. castaneum broad (Tcbr) mRNA, one peak at the end of feeding stage prior to the larvae entering the quiescent stage and another peak during the quiescent stage were detected in the whole body and midgut tissue dissected from staged insects. Expression of br during the final instar larval stage is essential for successful larval-pupal metamorphosis, because, RNAi-mediated knock-down of Tcbr during this stage derailed larval-pupal metamorphosis and produced insects that showed larval, pupal and adult structures. Tcbr dsRNA injected into the final instar larvae caused reduction in the mRNA levels of genes known to be involved in 20E action (EcRA, E74 and E75B). Tcbr dsRNA injected into the final instar larvae also caused an increase in the mRNA levels of JH-response genes (JHE and Kr-h1b). Knock-down of Tcbr expression also affected 20E-mediated remodeling of midgut during larval-pupal metamorphosis. These data suggest that the expression of Tcbr during the final instar larval stage promotes pupal program while suppressing the larval and adult programs ensuring a transitory pupal stage in holometabolous insects.
Figures
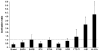



Similar articles
-
Krüppel homolog 1, an early juvenile hormone-response gene downstream of Methoprene-tolerant, mediates its anti-metamorphic action in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum.Dev Biol. 2009 Jan 15;325(2):341-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.016. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19013451
-
The Occurrence of the Holometabolous Pupal Stage Requires the Interaction between E93, Krüppel-Homolog 1 and Broad-Complex.PLoS Genet. 2016 May 2;12(5):e1006020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006020. eCollection 2016 May. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27135810 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor E93 specifies adult metamorphosis in hemimetabolous and holometabolous insects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 May 13;111(19):7024-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1401478111. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24778249 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel homolog 1 and E93: The doorkeeper and the key to insect metamorphosis.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020 Mar;103(3):e21609. doi: 10.1002/arch.21609. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31385626 Review.
-
Insights into the molecular basis of the hormonal control of molting and metamorphosis from Manduca sexta and Drosophila melanogaster.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Dec;33(12):1327-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2003.06.001. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14599504 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of E93 knockdown on female reproduction in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020 Aug;104(4):e21688. doi: 10.1002/arch.21688. Epub 2020 May 11. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32394503 Free PMC article.
-
TGFß/activin-dependent activation of Torso controls the timing of the metamorphic transition in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum.PLoS Genet. 2023 Nov 27;19(11):e1010897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010897. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 38011268 Free PMC article.
-
Where did the pupa come from? The timing of juvenile hormone signalling supports homology between stages of hemimetabolous and holometabolous insects.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 Oct 14;374(1783):20190064. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0064. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31438814 Free PMC article.
-
Kr-h1, a Cornerstone Gene in Insect Life History.Front Physiol. 2022 Apr 27;13:905441. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.905441. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35574485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular analysis of juvenile hormone analog action in controlling the metamorphosis of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2009 Jan;70(1):57-70. doi: 10.1002/arch.20288. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19072925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arakane Y, Muthukrishnan S, Kramer KJ, Specht CA, Tomoyasu Y, Lorenzen MD, Kanost M, Beeman RW. The Tribolium chitin synthase genes TcCHS1 and TcCHS2 are specialized for synthesis of epidermal cuticle and midgut peritrophic matrix. Insect Mol Biol. 2005;14:453–463. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M. Effects of juvenile hormone on adult differentiation of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1970;227:187–189. - PubMed
-
- Baker FC, Tsai LW, Reuter CC, Schooley DA. In vivo fluctuations of JH, JH acid, and ecdysteroid titer, and JH esterase activity during development of the fifth stadium Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. 1987;17:989–996.
-
- Bayer CA, von Kalm L, Fristrom JW. Relationships between protein isoforms and genetic functions demonstrate functional redundancy at the BroadComplex during Drosophila metamorphosis. Dev Biol. 1997;187:267–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

