Cardiotoxicity associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib
- PMID: 18083403
- PMCID: PMC2643085
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61865-0
Cardiotoxicity associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib
Abstract
Background: Sunitinib, a multitargeted tyrosine-kinase inhibitor, which is approved by both US and European Commission regulatory agencies for clinical use, extends survival of patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumours, but concerns have arisen about its cardiac safety. We therefore assessed the cardiovascular risk associated with sunitinib in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all cardiovascular events in 75 patients with imatinib-resistant, metastatic, gastrointestinal stromal tumours who had been enrolled in a phase I/II trial investigating the efficacy of sunitinib. The composite cardiovascular endpoint was cardiac death, myocardial infarction, and congestive heart failure. We also examined sunitinib's effects on left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and blood pressure. We investigated potential mechanisms of sunitinib-associated cardiac effects by studies in isolated rat cardiomyocytes and in mice.
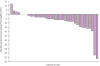
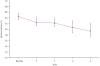
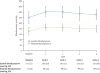
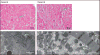
Findings: Eight of 75 (11%) patients given repeating cycles of sunitinib in the phase I/II trial had a cardiovascular event, with congestive heart failure recorded in six of 75 (8%). Ten of 36 (28%) patients treated at the approved sunitinib dose had absolute LVEF reductions in ejection fraction (EF) of at least 10%, and seven of 36 (19%) had LVEF reductions of 15 EF% or more. Sunitinib induced increases in mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and 35 of 75 (47%) individuals developed hypertension (>150/100 mm Hg). Congestive heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction generally responded to sunitinib being withheld and institution of medical management. Sunitinib caused mitochondrial injury and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in mice and in cultured rat cardiomyocytes.
Interpretation: Left ventricular dysfunction might be due, in part, to direct cardiomyocyte toxicity, exacerbated by hypertension. Patients treated with sunitinib should be closely monitored for hypertension and LVEF reduction, especially those with a history of coronary artery disease or cardiac risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Cardiac toxicity of sunitinib.Lancet. 2007 Dec 15;370(9604):1978-80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61840-6. Lancet. 2007. PMID: 18083385 No abstract available.
-
Cardiotoxicity associated with sunitinib.Lancet. 2008 Apr 12;371(9620):1244; author reply 1245. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60551-6. Lancet. 2008. PMID: 18406853 No abstract available.
-
Cardiotoxicity associated with sunitinib.Lancet. 2008 Apr 12;371(9620):1244-5; author reply 1245. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60552-8. Lancet. 2008. PMID: 18406854 No abstract available.
-
Sunitinib-related cardiotoxicity: an interdisciplinary issue.Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008 Jul;5(7):364-5. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio1222. Epub 2008 May 20. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008. PMID: 18490940 No abstract available.
References
-
- Krause D, Van Etten RA. Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:172–187. - PubMed
-
- Fabian MA, Biggs WH, 3rd, Treiber DK, Treiber DK, Atteridge CE, Azimioara MD, Benedetti MG, Carter TA, Ciceri P, Edeen PT, Floyd M, Ford JM, Galvin M, Gerlach JL, Grotzfeld RM, Herrgard S, Insko DE, Insko MA, Lai AG, Lélias JM, Mehta SA, Milanov ZV, Velasco AM, Wodicka LM, Patel HK, Zarrinkar PP, Lockhart DJ. A small molecule-kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(3):329–36. - PubMed
-
- Kerkelä R, Grazette L, Yacobi R, Iliescu C, Patten R, Beahm C, Walters B, Shevtsov S, Pesant S, Clubb FJ, Rosenzweig A, Salomon RN, Van Etten RA, Alroy J, Force T. Cardiotoxicity of the cancer therapeutic agent imatinib mesylate. Nat Med. 2006;12(8):908–16. - PubMed
-
- Mann DL. Targeted cancer therapeutics: the heartbreak of success. Nat Med. 2006;12(8):881–2. - PubMed
-
- Force T, Krause DS, Van Etten RA. Molecular mechanisms of cardiotoxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(5):332–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

