Cell wall polysaccharides are specifically involved in the exclusion of aluminum from the rice root apex
- PMID: 18083797
- PMCID: PMC2245838
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.111989
Cell wall polysaccharides are specifically involved in the exclusion of aluminum from the rice root apex
Abstract
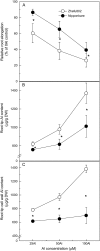
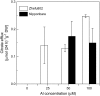
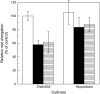
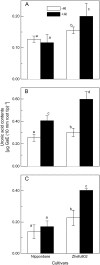
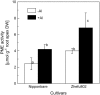
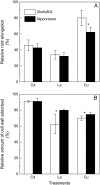
Rice (Oryza sativa) is the most aluminum (Al)-resistant crop species among the small-grain cereals, but the mechanisms responsible for this trait are still unclear. Using two rice cultivars differing in Al resistance, rice sp. japonica 'Nipponbare' (an Al-resistant cultivar) and rice sp. indica 'Zhefu802' (an Al-sensitive cultivar), it was found that Al content in the root apex (0-10 mm) was significantly lower in Al-resistant 'Nipponbare' than in sensitive 'Zhefu802', with more of the Al localized to cell walls in 'Zhefu802', indicating that an Al exclusion mechanism is operating in 'Nipponbare'. However, neither organic acid efflux nor changes in rhizosphere pH appear to be responsible for the Al exclusion. Interestingly, cell wall polysaccharides (pectin, hemicellulose 1, and hemicellulose 2) in the root apex were found to be significantly higher in 'Zhefu802' than in 'Nipponbare' in the absence of Al, and Al exposure increased root apex hemicellulose content more significantly in 'Zhefu802'. Root tip cell wall pectin methylesterase (PME) activity was constitutively higher in 'Zhefu802' than in 'Nipponbare', although Al treatment resulted in increased PME activity in both cultivars. Immunolocalization of pectins showed a higher proportion of demethylated pectins in 'Zhefu802', indicating a higher proportion of free pectic acid residues in the cell walls of 'Zhefu802' root tips. Al adsorption and desorption kinetics of root tip cell walls also indicated that more Al was adsorbed and bound Al was retained more tightly in 'Zhefu802', which was consistent with Al content, PME activity, and pectin demethylesterification results. These responses were specific to Al compared with other metals (CdCl(2), LaCl(3), and CuCl(2)), and the ability of the cell wall to adsorb these metals was also not related to levels of cell wall pectins. All of these results suggest that cell wall polysaccharides may play an important role in excluding Al specifically from the rice root apex.
Figures

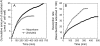
References
-
- Anthon GE, Barrett DM (2004) Comparison of three colorimetric reagents in the determination of methanol with alcohol oxidase. Application to the assay of pectin methylesterase. J Agric Food Chem 52 3749–3753 - PubMed
-
- Barcelo J, Poschenrieder C (2002) Fast root growth responses, root exudates, and internal detoxification as clues to the mechanisms of aluminium toxicity and resistance: a review. Environ Exp Bot 48 75–92
-
- Blamey FPC (2001) The role of the cell wall in aluminum toxicity. In N Ae, J Arihara, K Okada, A Srinivasan, eds, Plant Nutrient Acquisition: New Perspectives. Springer-Verlag, Tokyo, pp 201–226
-
- Blamey FPC, Edmeades DC, Wheeler DM (1990) Role of root cation-exchange capacity in differential aluminium tolerance of Lotus species. J Plant Nutr 13 729–744
-
- Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G (1973) New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem 54 484–489 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

