In vivo growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PAO1 and PA14 and the hypervirulent strain LESB58 in a rat model of chronic lung infection
- PMID: 18083816
- PMCID: PMC2293253
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01572-07
In vivo growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PAO1 and PA14 and the hypervirulent strain LESB58 in a rat model of chronic lung infection
Abstract
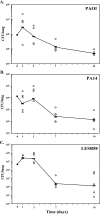
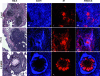
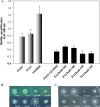
Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronic lung infections are the major cause of morbidity and mortality in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. The P. aeruginosa strains PAO1 and PA14 were compared with the Liverpool epidemic strain LESB58 to assess in vivo growth, infection kinetics, and bacterial persistence and localization within tissues in a rat model of chronic lung infection. The three P. aeruginosa strains demonstrated similar growth curves in vivo but differences in tissue distribution. The LESB58 strain persisted in the bronchial lumen, while the PAO1 and PA14 strains were found localized in the alveolar regions and grew as macrocolonies after day 7 postinfection. Bacterial strains were compared for swimming and twitching motility and for the production of biofilm. The P. aeruginosa LESB58 strain produced more biofilm than PAO1 and PA14. Competitive index (CI) analysis of PAO1, PA14, and LESB58 in vivo indicated CI values of 0.002, 0.0002, and 0.14 between PAO1-PA14, PAO1-LESB58, and LESB58-PA14, respectively. CI analysis comparing the in vivo growth of the PAO1 DeltaPA5441 mutant and four PA14 surface attachment-defective (sad) mutants gave CI values 10 to 1,000 times lower in competitions with their respective wild-type strains PAO1 and PA14. P. aeruginosa strains studied in the rat model of chronic lung infection demonstrated similar in vivo growth but differences in virulence as shown with a competitive in vivo assay. These differences were further confirmed with biofilm and motility in vitro assays, where strain LESB58 produced more biofilm but had less capacity for motility than PAO1 and PA14.
Figures


References
-
- Beuzon, C. R., and D. W. Holden. 2001. Use of mixed infections with Salmonella strains to study virulence genes and their interactions in vivo. Microbes Infect. 31345-1352. - PubMed
-
- Bragonzi, A., L. Wiehlmann, J. Klockgether, N. Cramer, D. Worlitzsch, G. Doring, and B. Tummler. 2006. Sequence diversity of the mucABD locus in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis. Microbiology 1523261-3269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

