A mutational analysis defines Vibrio fischeri LuxR binding sites
- PMID: 18083819
- PMCID: PMC2446796
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01443-07
A mutational analysis defines Vibrio fischeri LuxR binding sites
Abstract
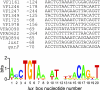
Vibrio fischeri quorum sensing involves the LuxI and LuxR proteins. The LuxI protein generates the quorum-sensing signal N-3-oxohexanoyl-l-homoserine lactone (3OC6-HSL), and LuxR is a signal-responsive transcriptional regulator which activates the luminescence (lux) genes and 17 other V. fischeri genes. For activation of the lux genes, LuxR binds to a 20-base-pair inverted repeat, the lux box, which is centered 42.5 base pairs upstream of the transcriptional start of the lux operon. Similar lux box-like elements have been identified in only a few of the LuxR-activated V. fischeri promoters. To better understand the DNA sequence elements required for LuxR binding and to identify binding sites in LuxR-regulated promoters other than the lux operon promoter, we have systematically mutagenized the lux box and evaluated the activity of many mutants. By doing so, we have identified nucleotides that are critical for promoter activity. Interestingly, certain lux box mutations allow a 3OC6-HSL-independent LuxR activation of the lux operon promoter. We have used the results of the mutational analysis to create a consensus lux box, and we have used this consensus sequence to identify LuxR binding sites in 3OC6-HSL-activated genes for which lux boxes could not be identified previously.
Figures




References
-
- Bassler, B. L., and R. Losick. 2006. Bacterially speaking. Cell 125237-246. - PubMed
-
- Bassler, B. L., M. Wright, and M. R. Silverman. 1994. Multiple signalling systems controlling expression of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi: sequence and function of genes encoding a second sensory pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 13273-286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

