Dysregulation of dopamine-dependent mechanisms as a determinant of hypertension: studies in dopamine receptor knockout mice
- PMID: 18083900
- PMCID: PMC4029502
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01036.2007
Dysregulation of dopamine-dependent mechanisms as a determinant of hypertension: studies in dopamine receptor knockout mice
Abstract
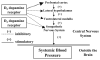
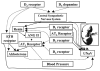
Dopamine plays an important role in the pathogenesis of hypertension by regulating epithelial sodium transport and by interacting with vasoactive hormones/humoral factors, such as aldosterone, angiotensin, catecholamines, endothelin, oxytocin, prolactin pro-opiomelancortin, reactive oxygen species, renin, and vasopressin. Dopamine receptors are classified into D(1)-like (D(1) and D(5)) and D(2)-like (D(2), D(3), and D(4)) subtypes based on their structure and pharmacology. In recent years, mice deficient in one or more of the five dopamine receptor subtypes have been generated, leading to a better understanding of the physiological role of each of the dopamine receptor subtypes. This review summarizes the results from studies of various dopamine receptor mutant mice on the role of individual dopamine receptor subtypes and their interactions with other G protein-coupled receptors in the regulation of blood pressure.
Figures
References
-
- Abell TJ, Richard AM, Ikram H, Espiner EA, Yandle Y. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;160:1392–1396. - PubMed
-
- Agnoli GC, Borgatti R, Cacciari M, Garutti C, Ikonomu E, Lenzi P. Antagonistic effects of sulpiride–racemic and enantiomers–on renal response to low-dose dopamine infusion in normal women. Nephron. 1989;51:491–498. - PubMed
-
- Agnoli GC, Cacciari M, Garutti C, Ikonomu E, Lenzi P, Marchetti G. Effects of extracellular fluid volume changes on renal response to low-dose dopamine infusion in normal women. Clin Physiol. 1987;7:465–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

