Impaired function of the phage-type RNA polymerase RpoTp in transcription of chloroplast genes is compensated by a second phage-type RNA polymerase
- PMID: 18084023
- PMCID: PMC2241911
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm1111
Impaired function of the phage-type RNA polymerase RpoTp in transcription of chloroplast genes is compensated by a second phage-type RNA polymerase
Abstract
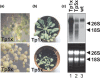
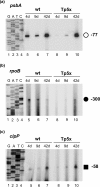
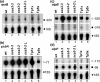
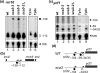
Although chloroplast genomes are small, the transcriptional machinery is very complex in plastids of higher plants. Plastidial genes of higher plants are transcribed by plastid-encoded (PEP) and nuclear-encoded RNA polymerases (NEP). The nuclear genome of Arabidopsis contains two candidate genes for NEP, RpoTp and RpoTmp, both coding for phage-type RNA polymerases. We have analyzed the use of PEP and NEP promoters in transgenic Arabidopsis lines with altered RpoTp activities and in Arabidopsis RpoTp insertion mutants lacking functional RpoTp. Low or lacking RpoTp activity resulted in an albino phenotype of the seedlings, which normalized later in development. Differences in promoter usage between wild type and plants with altered RpoTp activity were also most obvious early in development. Nearly all NEP promoters were used in plants with low or lacking RpoTp activity, though certain promoters showed reduced or even increased usage. The strong NEP promoter of the essential ycf1 gene, however, was not used in mutant seedlings lacking RpoTp activity. Our data provide evidence for NEP being represented by two phage-type RNA polymerases (RpoTp and RpoTmp) that have overlapping as well as gene-specific functions in the transcription of plastidial genes.
Figures

References
-
- Legen J, Wanner G, Herrmann RG, Small I, Schmitz-Linneweber C. Plastid tRNA genes trnC-GCA and trnN-GUU are essential for plant cell development. Plant J. 2007;51:751–762. - PubMed
-
- Shiina T, Tsunoyama Y, Nakahira Y, Khan MS. Plastid RNA polymerases, promoters, and transcription regulators in higher plants. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2005;244:1–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

