Preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of a tetrameric phospholipase A2 formed by two isoforms of crotoxin B from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom
- PMID: 18084096
- PMCID: PMC2344110
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309107058563
Preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of a tetrameric phospholipase A2 formed by two isoforms of crotoxin B from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom
Abstract
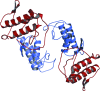
Crotoxin B is a basic phospholipase A2 found in the venom of Crotalus durissus terrificus and is one of the subunits that constitute crotoxin. This heterodimeric toxin, which is the main component of C. d. terrificus venom, is completed by an acidic, nontoxic and non-enzymatic component (crotoxin A) and is involved in important envenomation effects, such as neurological disorders, myotoxicity and renal failure. Although crotoxin was first crystallized in 1938, no crystal structure is currently available for crotoxin, crotoxin A or crotoxin B. In this work, the crystallization, X-ray diffraction data collection to 2.28 A resolution and molecular-replacement solution of a novel tetrameric complex formed by two dimers of crotoxin B isoforms (CB1 and CB2) is presented.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of crotoxin B from Crotalus durissus collilineatus venom.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009 Oct 1;65(Pt 10):1011-3. doi: 10.1107/S1744309109032631. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009. PMID: 19851009 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the role of oligomeric state on the biological activities of crotoxin: crystal structure of a tetrameric phospholipase A2 formed by two isoforms of crotoxin B from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom.Proteins. 2008 Aug 15;72(3):883-91. doi: 10.1002/prot.21980. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 18275084
-
Biochemical, functional, structural and phylogenetic studies on Intercro, a new isoform phospholipase A2 from Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom.Biochimie. 2013 Dec;95(12):2365-75. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.08.028. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 24035779
-
Crotoxin: novel activities for a classic beta-neurotoxin.Toxicon. 2010 Jun 1;55(6):1045-60. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2010.01.011. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Toxicon. 2010. PMID: 20109480 Review.
-
Crotoxin, half-century of investigations on a phospholipase A2 neurotoxin.Acta Physiol Pharmacol Latinoam. 1989;39(4):439-48. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Latinoam. 1989. PMID: 2562459 Review.
Cited by
-
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of crotoxin B from Crotalus durissus collilineatus venom.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009 Oct 1;65(Pt 10):1011-3. doi: 10.1107/S1744309109032631. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009. PMID: 19851009 Free PMC article.
-
Crotoxin B: Heterologous Expression, Protein Folding, Immunogenic Properties, and Irregular Presence in Crotalid Venoms.Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 31;14(6):382. doi: 10.3390/toxins14060382. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35737043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aird, S. D. & Kaiser, I. I. (1985). Toxicon, 23, 361–374. - PubMed
-
- Aird, S. D., Kaiser, I. I., Lewis, R. V. & Kruggel, W. G. (1985). Biochemistry, 24, 7054–7058. - PubMed
-
- Aird, S. D., Kaiser, I. I., Lewis, R. V. & Kruggel, W. G. (1986). Arch. Biochem. Biophys.249, 296–300. - PubMed
-
- Aird, S. D., Yates, J. R., Martino, P. A., Shabanowitz, J., Hunt, D. F. & Kaiser, I. I. (1990). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1040, 217–224. - PubMed
-
- Bon, C. (1997). Venom Phospholipase A2 Enzymes: Structure, Function and Mechanism, edited by R. M. Kini, pp. 269–285. Chichester: Wiley & Sons.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources