Activity-dependent gating of lateral inhibition in the mouse olfactory bulb
- PMID: 18084286
- PMCID: PMC2720685
- DOI: 10.1038/nn2030
Activity-dependent gating of lateral inhibition in the mouse olfactory bulb
Abstract
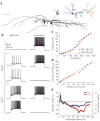
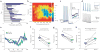
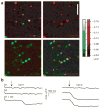
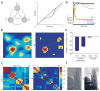
Lateral inhibition is a circuit motif found throughout the nervous system that often generates contrast enhancement and center-surround receptive fields. We investigated the functional properties of the circuits mediating lateral inhibition between olfactory bulb principal neurons (mitral cells) in vitro. We found that the lateral inhibition received by mitral cells is gated by postsynaptic firing, such that a minimum threshold of postsynaptic activity is required before effective lateral inhibition is recruited. This dynamic regulation allows the strength of lateral inhibition to be enhanced between cells with correlated activity. Simulations show that this regulation of lateral inhibition causes decorrelation of mitral cell activity that is evoked by similar stimuli, even when stimuli have no clear spatial structure. These results show that this previously unknown mechanism for specifying lateral inhibitory connections allows functional inhibitory connectivity to be dynamically remapped to relevant populations of neurons.
Figures
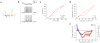
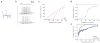
References
-
- Urban NN. Lateral inhibition in the olfactory bulb and in olfaction. Physiol Behav. 2002;77:607–612. - PubMed
-
- Friedrich RW, Laurent G. Dynamic optimization of odor representations by slow temporal patterning of mitral cell activity. Science. 2001;291:889–894. - PubMed
-
- Linster C, Sachse S, Galizia CG. Computational modeling suggests that response properties rather than spatial position determine connectivity between olfactory glomeruli. J Neurophysiol. 2005;93:3410–3417. - PubMed
-
- Kuffler SW. Discharge patterns and functional organization of mammalian retina. J Neurophysiol. 1953;16:37–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

