ITPKC functional polymorphism associated with Kawasaki disease susceptibility and formation of coronary artery aneurysms
- PMID: 18084290
- PMCID: PMC2876982
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2007.59
ITPKC functional polymorphism associated with Kawasaki disease susceptibility and formation of coronary artery aneurysms
Abstract
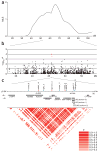
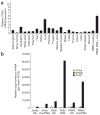
Kawasaki disease is a pediatric systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology for which a genetic influence is suspected. We identified a functional SNP (itpkc_3) in the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase C (ITPKC) gene on chromosome 19q13.2 that is significantly associated with Kawasaki disease susceptibility and also with an increased risk of coronary artery lesions in both Japanese and US children. Transfection experiments showed that the C allele of itpkc_3 reduces splicing efficiency of the ITPKC mRNA. ITPKC acts as a negative regulator of T-cell activation through the Ca2+/NFAT signaling pathway, and the C allele may contribute to immune hyper-reactivity in Kawasaki disease. This finding provides new insights into the mechanisms of immune activation in Kawasaki disease and emphasizes the importance of activated T cells in the pathogenesis of this vasculitis.
Figures

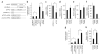

References
-
- Kawasaki T. Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes: my clinical observation (in Japanese) Jpn J Allergy. 1967;16:178–222. English translation by. - PubMed
- Shike H, Burns JC, Shimizu C, translators. Pediatr Infect Dis J. Vol. 21. 2002. pp. 993–995. - PubMed
-
- Kato H, Koike S, Yamamoto M, Ito Y, Yano E. Coronary aneurysms in infants and young children with acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. J Pediatr. 1975;86:892–898. - PubMed
-
- Kato H, et al. Long-term consequences of Kawasaki disease A 10- to 21-year follow-up study of 594 patients. Circulation. 1996;94:1379–1385. - PubMed
-
- Cook DH, et al. Results from an international survey of Kawasaki disease in 1979–82. Can J Cardiol. 1989;5:389–394. - PubMed
-
- Fujita Y, et al. Kawasaki disease in families. Pediatrics. 1989;84:666–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

