Vector and parameters for targeted transgenic RNA interference in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 18084299
- PMCID: PMC2290002
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth1146
Vector and parameters for targeted transgenic RNA interference in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
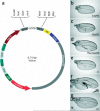
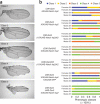
The conditional expression of hairpin constructs in Drosophila melanogaster has emerged in recent years as a method of choice in functional genomic studies. To date, upstream activating site-driven RNA interference constructs have been inserted into the genome randomly using P-element-mediated transformation, which can result in false negatives due to variable expression. To avoid this problem, we have developed a transgenic RNA interference vector based on the phiC31 site-specific integration method.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

