In vivo molecular imaging to diagnose and subtype tumors through receptor-targeted optically labeled monoclonal antibodies
- PMID: 18084609
- PMCID: PMC2134899
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.07787
In vivo molecular imaging to diagnose and subtype tumors through receptor-targeted optically labeled monoclonal antibodies
Abstract
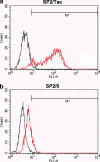
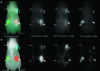
Molecular imaging of cell surface receptors can potentially diagnose tumors based on their distinct expression profiles. Using multifilter spectrally resolved optical imaging with three fluorescently labeled antibodies, we simultaneously imaged three different cell surface receptors to distinguish tumor types noninvasively. We selected tumors overexpressing different subtypes of EGFR receptor: HER-1 (A431) and HER-2 (NIH3T3/HER2(+)), or interleukin-2 receptor alpha-subunit receptor (IL-2Ralpha; SP2/Tac). After tumor establishment, a cocktail of three fluorescently labeled monoclonal antibodies was injected: cetuximab-Cy5 (targetingHER-1), trastuzumab-Cy7(HER-2),anddaclizumab-AlexaFluor-700 (IL-2Ra). Optical fluorescence imaging was performed after 24 hours with both a red filter set and three successive filter sets (yellow, red, and deep red). Spectrally resolved imaging of 10 mice clearly distinguished A431, NIH3T3/HER2(+), and SP2-Tac tumors based on their distinct optical spectra. Three-filter sets significantly increased the signal-to-background ratio compared to a single-filter set by reducing the background signal, thus significantly improving the differentiation of each of the receptors targeted (P < .022). In conclusion, following multifilter spectrally resolved imaging, different tumor types can be simultaneously distinguished and diagnosed in vivo. Multiple filter sets increase the signal-to-noise ratio by substantially reducing the background signal, and may allow more optical dyes to be resolved within the narrow limits of the near-infrared spectrum.
Keywords: Growth factor receptor; antibody cocktail; contrast agent; near-infrared; optical imaging.
Figures



References
-
- Hoffman RM. The multiple uses of fluorescent proteins to visualize cancer in vivo. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:796–806. - PubMed
-
- Barrett T, Koyama Y, Hama Y, Ravizzini G, Shin IS, Jang B-S, Paik CH, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. Molecular imaging for typing epidermal growth factor receptors expressed on tumor cells using a cocktail of two monoclonal antibodies conjugated with two distinct near infrared fluorophores. Clin Cancer Res. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Cohen BD, Siegall CB, Bacus S, Foy L, Green JM, Hellstrom I, Hellstrom KE, Fell HP. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor family members in growth and differentiation of breast carcinoma. Biochem Soc Symp. 1998;63:199–210. - PubMed
-
- Souder C, Leitzel K, Ali SM, Demers L, Evans DB, Chaudri-Ross HA, Hackl W, Hamer P, Carney W, Lipton A. Serum epidermal growth factor receptor/HER-2 predicts poor survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Cancer. 2006;107:2337–2345. - PubMed
-
- Carrington C. Optical imaging sheds light on cancer's signature-regional blood flow and tissue oxygenization measures may permit earlier breast cancer detection. Diagn Imaging. 2004. June: http://www.diagnostic imaging.com/molecularimagingoutlook/2004jun/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
