Neuropharmacology of the endocannabinoid signaling system-molecular mechanisms, biological actions and synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 18084639
- PMCID: PMC2139910
- DOI: 10.2174/157015907780866910
Neuropharmacology of the endocannabinoid signaling system-molecular mechanisms, biological actions and synaptic plasticity
Abstract
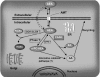
The endocannabinoid signaling system is composed of the cannabinoid receptors; their endogenous ligands, the endocannabinoids; the enzymes that produce and inactivate the endocannabinoids; and the endocannabinoid transporters. The endocannabinoids are a new family of lipidic signal mediators, which includes amides, esters, and ethers of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Endocannabinoids signal through the same cell surface receptors that are targeted by Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta(9)THC), the active principles of cannabis sativa preparations like hashish and marijuana. The biosynthetic pathways for the synthesis and release of endocannabinoids are still rather uncertain. Unlike neurotransmitter molecules that are typically held in vesicles before synaptic release, endocannabinoids are synthesized on demand within the plasma membrane. Once released, they travel in a retrograde direction and transiently suppress presynaptic neurotransmitter release through activation of cannabinoid receptors. The endocannabinoid signaling system is being found to be involved in an increasing number of pathological conditions. In the brain, endocannabinoid signaling is mostly inhibitory and suggests a role for cannabinoids as therapeutic agents in central nervous system (CNS) disease. Their ability to modulate synaptic efficacy has a wide range of functional consequences and provides unique therapeutic possibilities. The present review is focused on new information regarding the endocannabinoid signaling system in the brain. First, the structure, anatomical distribution, and signal transduction mechanisms of cannabinoid receptors are described. Second, the synthetic pathways of endocannabinoids are discussed, along with the putative mechanisms of their release, uptake, and degradation. Finally, the role of the endocannabinoid signaling system in the CNS and its potential as a therapeutic target in various CNS disease conditions, including alcoholism, are discussed.
Keywords: Alcoholism; CB1 receptors; CNS; alcohol-drinking behavior; endocannabinoids; reward; synaptic plasticity; therapy.
Figures

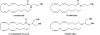





Similar articles
-
Endocannabinoids and synaptic function in the CNS.Neuroscientist. 2007 Apr;13(2):127-37. doi: 10.1177/1073858406296716. Neuroscientist. 2007. PMID: 17404373 Review.
-
Role of endogenous cannabinoids in synaptic signaling.Physiol Rev. 2003 Jul;83(3):1017-66. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00004.2003. Physiol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12843414 Review.
-
The neuropharmacology of cannabinoid receptor ligands in central signaling pathways.Eur J Neurosci. 2022 Feb;55(4):909-921. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14982. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Eur J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 32974975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocannabinoids and their actions.Vitam Horm. 2002;65:225-55. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(02)65066-6. Vitam Horm. 2002. PMID: 12481549 Review.
-
Endocannabinoid system: emerging role from neurodevelopment to neurodegeneration.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009 Apr;9(4):448-62. doi: 10.2174/138955709787847921. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19356123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptations of striatal endocannabinoid system during stress.Mol Neurobiol. 2009 Jun;39(3):178-84. doi: 10.1007/s12035-009-8061-4. Epub 2009 Mar 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19267225 Review.
-
The influence of genetics on the endocannabinoid system gene expression and relevance for targeting reproductive conditions.J Cannabis Res. 2025 May 29;7(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s42238-025-00275-x. J Cannabis Res. 2025. PMID: 40442827 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of cellular redox homeostasis by the endocannabinoid system.Open Biol. 2016 Apr;6(4):150276. doi: 10.1098/rsob.150276. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Open Biol. 2016. PMID: 27248801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The endocannabinoid system: 'NO' longer anonymous in the control of nitrergic signalling?J Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Apr 1;9(2):91-103. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjx008. J Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28130308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of catecholamines in modulating responses to stress: Sex-specific patterns, implications, and therapeutic potential for post-traumatic stress disorder and opiate withdrawal.Eur J Neurosci. 2020 Jul;52(1):2429-2465. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14714. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Eur J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32125035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abood ME, Ditto KE, Noel MA, Showalter VM, Tao Q. Isolation and expression of a mouse CB1 cannabinoid receptor gene. Comparison of binding properties with those of native CB1 receptors in mouse brain and N18TG2 neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997;53:207–214. - PubMed
-
- Akinshola BE, Chakrabarti A, Onaivi ES. In-vitro and in-vivo action of cannabinoids. Neurochem Res. 1999;24:1233–1240. - PubMed
-
- Akinshola BE, Taylor RE, Ogunseitan AB, Onaivi ES. Anandamide inhibition of recombinant AMPA receptor subunits in Xenopus oocytes is increased by forskolin and 8-bromo-cyclic AMP. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1999;360:242–248. - PubMed
-
- Alger BE. Retrograde signaling in the regulation of synaptic transmission: focus on endocannabinoids. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;68:247–286. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
