An epidemic of chronic pseudophakic endophthalmitis due to Ochrobactrum anthropi: clinical findings and managements of nine consecutive cases
- PMID: 18085486
- PMCID: PMC2430177
- DOI: 10.1080/09273940701798546
An epidemic of chronic pseudophakic endophthalmitis due to Ochrobactrum anthropi: clinical findings and managements of nine consecutive cases
Abstract
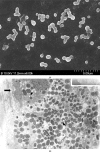
Purpose: To report an epidemic of O. anthropi pseudophakic endophthalmitis.
Methods: The medical records of nine patients with culture-proven O. anthropi endophthalmitis were reviewed.
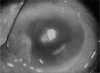
Results: The presenting features were compatible to chronic endophthalmitis. Two patients showed coinfections with P. acnes. Antibiotics sensitivity test revealed susceptibility to quinolones. Pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) with partial capsulectomy (PC) cured infections in seven patients without coinfection of P. acnes. Final visual acuity was 20/40 or better in five patients.
Conclusions: O. anthropi should be considered in cases with chronic pseudophakic endophthalmitis. PPV with PC should be the initial therapeutic option for O. anthropi endophthalmitis.
Figures

References
-
- Fox GM, Jooneph BC, Flynn HW. Delayed-onset pseudophakic endophthalmitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991;111:163–173. - PubMed
-
- Aldave AJ, Stein JD, Deramo VA, et al. Treatment strategies for postoperative Propionibacterium acnes endophthalmitis. Ophthalmology. 1999;106:2395–2401. - PubMed
-
- Clark WL, Kaiser PK, Flynn HW, et al. Treatment strategies and visual acuity outcomes in chronic postoperative Propionibacterium acnes endophthalmitis. Ophthalmology. 1999;106:1665–1670. - PubMed
-
- Stern WH, Tamura E, Jacobs RA, et al. Epidemic postsurgical Candida parapsilosis endophthalmitis. Clinical findings and management of 15 consecutive cases. Ophthalmology. 1985;92:1701–1709. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
