Differential effects of black raspberry and strawberry extracts on BaPDE-induced activation of transcription factors and their target genes
- PMID: 18085529
- PMCID: PMC3758121
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.20377
Differential effects of black raspberry and strawberry extracts on BaPDE-induced activation of transcription factors and their target genes
Abstract
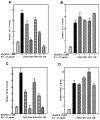
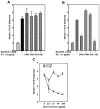
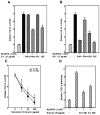
The chemopreventive properties of edible berries have been demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo, however, the specific molecular mechanisms underlying their anti-cancer effects are largely unknown. Our previous studies have shown that a methanol extract fraction of freeze-dried black raspberries inhibits benzoapyrene (BaP)-induced transformation of Syrian hamster embryo cells. This fraction also blocks activation of activator protein-1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) induced by benzoapyrene diol-epoxide (BaPDE) in mouse epidermal JB6 Cl 41 cells. To determine if different berry types exhibit specific mechanisms for their anti-cancer effects, we compared the effects of extract fractions from both black raspberries and strawberries on BaPDE-induced activation of various signaling pathways in Cl 41 cells. Black raspberry fractions inhibited the activation of AP-1, NF-kappaB, and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) by BaPDE as well as their upstream PI-3K/Akt-p70(S6K) and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. In contrast, strawberry fractions inhibited NFAT activation, but did not inhibit the activation of AP-1, NF-kappaB or the PI-3K/Akt-p70(S6K) and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Consistent with the effects on NFAT activation, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) induction by BaPDE was blocked by extract fractions of both black raspberries and strawberries, whereas vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, which depends on AP-1 activation, was suppressed by black raspberry fractions but not strawberry fractions. These results suggest that black raspberry and strawberry components may target different signaling pathways in exerting their anti-carcinogenic effects.
(c) 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Black raspberry extracts inhibit benzo(a)pyrene diol-epoxide-induced activator protein 1 activation and VEGF transcription by targeting the phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway.Cancer Res. 2006 Jan 1;66(1):581-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1951. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16397275
-
Inhibition of benzo(a)pyrene diol-epoxide-induced transactivation of activated protein 1 and nuclear factor kappaB by black raspberry extracts.Cancer Res. 2002 Dec 1;62(23):6857-63. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12460899
-
Differential inhibition of UV-induced activation of NF kappa B and AP-1 by extracts from black raspberries, strawberries, and blueberries.Nutr Cancer. 2007;58(2):205-12. doi: 10.1080/01635580701328453. Nutr Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17640167
-
The role of AP-1, NF-kappaB and ROS/NOS in skin carcinogenesis: the JB6 model is predictive.Mol Cell Biochem. 2002 May-Jun;234-235(1-2):185-93. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12162432 Review.
-
Activator protein 1 (AP-1)- and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-dependent transcriptional events in carcinogenesis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2000 May 1;28(9):1338-48. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00220-3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000. PMID: 10924853 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Ingredients with Health-Promoting Properties of Strawberry Fruit (Fragaria x ananassa Duchesne).Molecules. 2023 Mar 17;28(6):2711. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062711. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of freeze-dried black raspberry powder in ulcerative colitis.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Mar;32(3):343-50. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq248. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21098643 Free PMC article.
-
Blueberry phytochemicals inhibit growth and metastatic potential of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through modulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway.Cancer Res. 2010 May 1;70(9):3594-605. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3565. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20388778 Free PMC article.
-
Urolithin A suppresses the proliferation of endometrial cancer cells by mediating estrogen receptor-α-dependent gene expression.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016 Nov;60(11):2387-2395. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600048. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016. PMID: 27342949 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for quantification of four anthocyanins and its application in a clinical pharmacology study of a bioadhesive black raspberry gel.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009 Dec 1;877(31):4027-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.10.026. Epub 2009 Oct 30. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19896910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heber D. Vegetables, fruits and phytoestrogens in the prevention of diseases. J Postgrad Med. 2004;50:145–149. - PubMed
-
- Heggie SJ, Wiseman MJ, Cannon GJ, et al. Defining the state of knowledge with respect to food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer. J Nutr. 2003:3837S–3842. - PubMed
-
- Genkinger JM, Platz EA, Hoffman SC, Comstock GW, Helzlsouer KJ. Fruit, vegetable, and antioxidant intake and all-cause, cancer, and cardiovascular disease mortality in a community-dwelling population in Washington county, Maryland. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;160:1223–1233. - PubMed
-
- Xue H, Aziz RM, Sun N, et al. Inhibition of cellular transformation by berry extracts. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22:351–356. - PubMed
-
- Kresty LA, Morse MA, Morgan C, et al. Chemoprevention of esophageal tumorigenesis by dietary administration of lyophilized black raspberries. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6112–6119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

