Experience-induced fetal plasticity: the effect of gestational ethanol exposure on the behavioral and neurophysiologic olfactory response to ethanol odor in early postnatal and adult rats
- PMID: 18085882
- PMCID: PMC3436600
- DOI: 10.1037/0735-7044.121.6.1293
Experience-induced fetal plasticity: the effect of gestational ethanol exposure on the behavioral and neurophysiologic olfactory response to ethanol odor in early postnatal and adult rats
Abstract
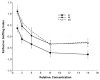
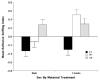
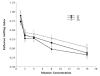
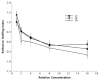
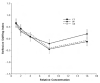
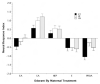
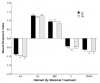
Human fetal ethanol exposure is strongly associated with ethanol avidity during adolescence. Evidence that intrauterine olfactory experience influences chemosensory-guided postnatal behaviors suggests that an altered response to ethanol odor resulting from fetal exposure may contribute to later abuse risk. Using behavioral and neurophysiological methods, the authors tested whether ethanol exposure via the dam's diet resulted in an altered responsiveness to ethanol odor in infant and adult rats. Compared with controls, (a) fetal exposure tuned the neurophysiologic response of the olfactory epithelium to ethanol odor at some expense to its responsiveness to other odorants in infantile rats--this effect was absent in adults; (b) the neural effect in infantile rats was paralleled by an altered behavioral response to ethanol odor that was specific to this odorant--this effect was also absent in adults; and (c) a significant component of the infantile behavioral effect was attributable to ethanol's effect on the olfactory neural modality. These data provide evidence for an important relationship between prenatal ethanol experience and postnatal behavioral responsiveness to the drug that is modulated or determined by olfactory function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ontogeny of the enhanced fetal-ethanol-induced behavioral and neurophysiologic olfactory response to ethanol odor.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010 Feb;34(2):206-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01083.x. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010. PMID: 19951301 Free PMC article.
-
Gestational naltrexone ameliorates fetal ethanol exposures enhancing effect on the postnatal behavioral and neural response to ethanol.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012 Oct;237(10):1197-208. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2012.012132. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012. PMID: 23045720 Free PMC article.
-
Gestational ethanol exposure alters the behavioral response to ethanol odor and the expression of neurotransmission genes in the olfactory bulb of adolescent rats.Brain Res. 2009 Feb 3;1252:105-16. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.11.023. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19063871 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal or infantile exposure to ethanol promotes ethanol ingestion in adolescence and adulthood: a theoretical review.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Jun;29(6):909-29. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000171046.78556.66. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 15976517 Review.
-
Exposure to low and moderate doses of alcohol on late gestation modifies infantile response to and preference for alcohol in rats.Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2006;42(1):22-30. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2006. PMID: 16801722 Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal Ethanol Exposure and Whisker Clipping Disrupt Ultrasonic Vocalizations and Play Behavior in Adolescent Rats.Brain Sci. 2016 Sep 28;6(4):43. doi: 10.3390/brainsci6040043. Brain Sci. 2016. PMID: 27690116 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of gestational and postnatal ethanol experience on the adolescent and adult odor-mediated responses to ethanol in observer and demonstrator rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010 Oct;34(10):1705-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01257.x. Epub 2010 Jul 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010. PMID: 20608909 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent ethanol experience alters immediate and long-term behavioral responses to ethanol odor in observer and demonstrator rats.Behav Brain Funct. 2009 Jun 4;5:23. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-5-23. Behav Brain Funct. 2009. PMID: 19497110 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal exposure to ethanol affects postnatal neurogenesis in thalamus.Exp Neurol. 2010 Jun;223(2):566-73. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.02.003. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Exp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20170653 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogeny of the enhanced fetal-ethanol-induced behavioral and neurophysiologic olfactory response to ethanol odor.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010 Feb;34(2):206-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01083.x. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010. PMID: 19951301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abate P, Pepino MY, Dominguez HD, Spear NE, Molina JC. Fetal associative learning mediated through maternal alcohol intoxication. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2000;24:39–47. - PubMed
-
- Abate P, Spear NE, Molina JC. Fetal and infantile alcohol-mediated associative learning in the rat. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2001;25:989–998. - PubMed
-
- Abel EL, York JL. Absence of effect of prenatal ethanol on adult emotionality and ethanol consumption in rats. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1979;40:547–553. - PubMed
-
- Alati R, Al Mamum A, Williams GM, O’Callagham M, Najman JM, Bor W. In utero alcohol exposure and prediction of alcohol disorders in early adulthood: A birth cohort study. Archive of General Psychiatry. 2006;63:1009–1016. - PubMed
-
- Baer JS, Bar HM, Bookstein FL, Sampson PD, Streissguth AP. Prenatal alcohol exposure and family history of alcoholism in the etiology of adolescent alcohol problems. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1998;59:533–543. - PubMed

