A randomized controlled trial of a parent-centered intervention in preventing substance use and HIV risk behaviors in Hispanic adolescents
- PMID: 18085908
- PMCID: PMC3743679
- DOI: 10.1037/0022-006X.75.6.914
A randomized controlled trial of a parent-centered intervention in preventing substance use and HIV risk behaviors in Hispanic adolescents
Abstract
The present study evaluated the efficacy of Familias Unidas + Parent-Preadolescent Training for HIV Prevention (PATH), a Hispanic-specific, parent-centered intervention, in preventing adolescent substance use and unsafe sexual behavior. Two hundred sixty-six 8th-grade Hispanic adolescents and their primary caregivers were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 conditions: Familias Unidas + PATH, English for Speakers of Other Languages (ESOL) + PATH, and ESOL + HeartPower! for Hispanics (HEART). Participants were assessed at baseline and at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months postbaseline. Results showed that (a) Familias Unidas + PATH was efficacious in preventing and reducing cigarette use relative to both control conditions; (b) Familias Unidas + PATH was efficacious, relative to ESOL + HEART, in reducing illicit drug use; and (c) Familias Unidas + PATH was efficacious, relative to ESOL + PATH, in reducing unsafe sexual behavior. The effects of Familias Unidas + PATH on these distal outcomes were partially mediated by improvements in family functioning. These findings suggest that strengthening the family system, rather than targeting specific health behaviors, may be most efficacious in preventing and/or reducing cigarette smoking, illicit drug use, and unsafe sex in Hispanic adolescents.
(Copyright) 2007 APA.
Figures

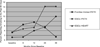
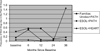
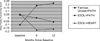
Comment in
-
Family-Based Interventions in Preventing Children and Adolescents from Using Tobacco: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Acad Pediatr. 2016 Jul;16(5):419-429. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2015.12.006. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Acad Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26892909 Review.
Similar articles
-
A randomized controlled trial of Familias Unidas for Hispanic adolescents with behavior problems.Psychosom Med. 2009 Nov;71(9):987-95. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e3181bb2913. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Psychosom Med. 2009. PMID: 19834053 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of a family intervention in reducing HIV risk behaviors among high-risk Hispanic adolescents: a randomized controlled trial.Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012 Feb;166(2):127-33. doi: 10.1001/archpediatrics.2011.189. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012. PMID: 21969363 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rationale and design for eHealth Familias Unidas Primary Care: A drug use, sexual risk behavior, and STI preventive intervention for hispanic youth in pediatric primary care clinics.Contemp Clin Trials. 2019 Jan;76:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Contemp Clin Trials. 2019. PMID: 30453076 Free PMC article.
-
For Whom Do Parenting Interventions to Prevent Adolescent Substance Use Work?Prev Sci. 2018 May;19(4):570-578. doi: 10.1007/s11121-017-0853-6. Prev Sci. 2018. PMID: 29150747 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention induced changes on parenting practices, youth self-pride and sexual norms to reduce HIV-related behaviors among rural African American youths.J Youth Adolesc. 2011 Sep;40(9):1147-63. doi: 10.1007/s10964-011-9642-x. Epub 2011 Mar 5. J Youth Adolesc. 2011. PMID: 21373904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A computational future for preventing HIV in minority communities: how advanced technology can improve implementation of effective programs.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013 Jun 1;63 Suppl 1(0 1):S72-84. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31829372bd. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013. PMID: 23673892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventing Youth Internalizing Symptoms Through the Familias Unidas Intervention: Examining Variation in Response.Prev Sci. 2018 Feb;19(Suppl 1):49-59. doi: 10.1007/s11121-016-0666-z. Prev Sci. 2018. PMID: 27318951 Free PMC article.
-
eHealth Familias Unidas: Efficacy Trial of an Evidence-Based Intervention Adapted for Use on the Internet with Hispanic Families.Prev Sci. 2019 Jan;20(1):68-77. doi: 10.1007/s11121-018-0905-6. Prev Sci. 2019. PMID: 29748900 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluating the Short-term Impact of Media Aware Parent, a Web-based Program for Parents with the Goal of Adolescent Sexual Health Promotion.J Youth Adolesc. 2019 Sep;48(9):1686-1706. doi: 10.1007/s10964-019-01077-0. Epub 2019 Jul 14. J Youth Adolesc. 2019. PMID: 31304562 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A qualitative view of drug use behaviors of Mexican male injection drug users deported from the United States.J Urban Health. 2011 Feb;88(1):104-17. doi: 10.1007/s11524-010-9508-7. J Urban Health. 2011. PMID: 21246301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Heart Association. Heartpower: Learn it! Live it! Love it!: A teacher resource [American Heart Association Schoolsite Program] Washington, DC: Author; 1996.
-
- Arnett JJ. Emerging adulthood: The winding road from the late teens through the twenties. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press; 2004. - PubMed
-
- Barnes HL, Olson DH. Parent-adolescent communication and the circumplex model. Child Development. 1985;56:438–447.
-
- Bean FD, Corona R, Tuiran R, Woodrow-Lafield KA, Van Hook J. Circular, invisible, and ambiguous migrants: Components of difference in estimates of the number of unauthorized Mexican migrants in the United States. Demography. 2001;38:411–422. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein R. Minority population tops 100 million. 2007 Retrieved May 17, 2007, from http://www.census.gov/dcmd/www/embargo/popest/national/pio-nat_stat.html.

