Pitfalls in diagnosing a small cystic insulinoma: a case report
- PMID: 18086310
- PMCID: PMC2245958
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-1-181
Pitfalls in diagnosing a small cystic insulinoma: a case report
Abstract
Insulinoma is a rare pancreatic endocrine tumour and is typically sporadic and solitary. Over 90% of all insulinomas are benign. Cystic insulinomas are also rare. It is not difficult to determine the site of such neoplasm, as cystic insulinomas are usually 4-10 cm in diameter. We present the case of a patient with a histologically confirmed cystic insulinoma diagnosed after approximately 10 years of hypoglycaemia symptoms. This case is unique because of the small size (2.2 cm) of the tumour. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) was useful for localizing this tumour.
Figures
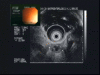

Similar articles
-
Small cystic insulinoma: value of arterial stimulation venous sampling.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1997 Jul-Aug;20(4):308-10. doi: 10.1007/BF02743540. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1997. PMID: 9211780
-
Insulinoma: a quarter century of dietary control.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2022 Sep 1;2022:22-0270. doi: 10.1530/EDM-22-0270. Online ahead of print. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36137190 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in clinical characteristics, treatment, and outcomes of sporadic and MEN-1-related insulinomas.Endokrynol Pol. 2023 Jul 11. doi: 10.5603/EP.a2023.0049. Online ahead of print. Endokrynol Pol. 2023. PMID: 37431872
-
Insulinoma: case report and review of diagnostic and treatment modalities.J Assoc Physicians India. 2013 Jun;61(6):423-6. J Assoc Physicians India. 2013. PMID: 24640215 Review.
-
[Utility of endoscopic ultrasonography on localization of insulinomas. Case report and review of the literature].J Med Liban. 2004 Jul-Sep;52(3):165-7. J Med Liban. 2004. PMID: 16432975 Review. French.
References
-
- Service FJ, McMahon MM, O'Brien PC, Ballard DJ. Functioning insulinoma: incidence, recurrence and long-survival of patients: a 60-year study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1991;66:711–719. - PubMed
-
- Lack EE. Pancreatic endocrine neoplasms. In: Lack EE, editor. Pathology of pancreas, gallbladder, extrahepatic biliary tract and ampullary region. New York: Oxford University Press; 2003. pp. 323–373.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

