The impact of a reduced dose of dexamethasone on glucose control after coronary artery bypass surgery
- PMID: 18086312
- PMCID: PMC2235839
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-6-39
The impact of a reduced dose of dexamethasone on glucose control after coronary artery bypass surgery
Abstract
Background: Intensive insulin therapy to maintain normoglycemia after cardiac surgery reduces morbidity and mortality. We investigated the magnitude and duration of hyperglycemia caused by dexamethasone administered after cardiopulmonary bypass.
Methods: A single-center before-after cohort study was performed. All consecutive patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting with cardiopulmonary bypass during a 6-month period were included. Insulin administration was guided by a sliding scale protocol. Halfway the observation period, the dexamethasone protocol was changed. The single dose (1D) group received a pre-operative dose of dexamethasone of 1 mg/kg. The double dose group (2D) received an additional dose of 0.5 mg/kg of dexamethasone post-operatively at ICU admission.
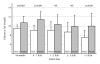
Results: We included 116 patients in the 1D group and 158 patients in the 2D group. There were no significant baseline differences between the groups. Median Euroscore was 5. In univariable analysis, the glucose level was different between groups 1D and 2D at 4, 6, 9, 12 and 24 hours after ICU admission (all p < 0.001). Insulin infusion was higher in the 1D group. Corrected for insulin dose in multivariable linear analysis, the difference in glucose between the 1D and 2D groups was 1.5 mmol/L (95% confidence interval 1.0-2.0, p < 0.001) 12 hours after ICU admission.
Conclusion: Dexamethasone exerts a hyperglycemic effect in cardiac surgery patients. Patients receiving high-dose corticosteroid therapy should be monitored and treated more intensively for hyperglycemic episodes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of high-dose dexamethasone on perioperative lactate levels and glucose control: a randomized controlled trial.Crit Care. 2015 Feb 13;19(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0736-9. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25886901 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dexamethasone: benefit and prejudice for patients undergoing on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: a study on myocardial, pulmonary, renal, intestinal, and hepatic injury.Chest. 2005 Oct;128(4):2677-87. doi: 10.1378/chest.128.4.2677. Chest. 2005. PMID: 16236942 Clinical Trial.
-
Intensive insulin therapy does not alter the inflammatory response in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: a randomized controlled trial [ISRCTN95608630].Crit Care. 2005;9(6):R790-7. doi: 10.1186/cc3911. Epub 2005 Nov 16. Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 16356228 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of insulin and pro-inflammatory effects of glucose: relevance to the management of acute myocardial infarction and other acute coronary syndromes.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2006;7 Suppl 2:S25-34. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2006. PMID: 17224874 Review.
-
Impact of Intraoperative Dexamethasone on Perioperative Blood Glucose Levels: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials.Anesth Analg. 2024 Sep 1;139(3):490-508. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000006933. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Anesth Analg. 2024. PMID: 39151135
Cited by
-
Prophylactic corticosteroids for cardiopulmonary bypass in adult cardiac surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Mar 20;3(3):CD005566. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005566.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38506343 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone-induced hyperglycaemia in COVID-19: Glycaemic profile in patients without diabetes and factors associated with hyperglycaemia.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022 Dec;194:110151. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110151. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 36375566 Free PMC article.
-
Association between intraoperative hyperglycemia and postoperative end-organ dysfunctions after cardiac surgery: a retrospective observational study.J Anesth. 2022 Apr;36(2):174-184. doi: 10.1007/s00540-021-03024-5. Epub 2021 Nov 22. J Anesth. 2022. PMID: 34807289
-
Effect of low-dose dexamethasone on extra vascular lung water in patients following on-pump elective primary coronary artery bypass graft surgery.Ann Card Anaesth. 2019 Oct-Dec;22(4):372-378. doi: 10.4103/aca.ACA_122_18. Ann Card Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 31621671 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Eagle KA, Guyton RA, Davidoff R, Edwards FH, Ewy GA, Gardner TJ, Hart JC, Herrmann HC, Hillis LD, Hutter AM, Lytle BW, Marlow RA, Nugent WC, Orszulak TA, American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association ACC/AHA 2004 guideline update for coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee to Update the 1999 Guidelines for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery) Circulation. 2004;110:e340–e437. - PubMed
-
- Kusumanto YH, Tio RA, Loef BG, Sluiter WJ, Mulder NH, Hospers GA. Systemic VEGF levels after coronary artery bypass graft surgery reflects the extent of inflammatory response. Acute Card Care. 2006;8:41–45. - PubMed
-
- Nathoe HM, van Dijk D, Jansen EW, Suyker WJ, Diephuis JC, van Boven WJ, De la Rivière AB, Borst C, Kalkman CJ, Grobbee DE, Buskens E, De Jaegere PP, Octopus Study Group A comparison of on-pump and off-pump coronary bypass surgery in low-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:394–402. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021775. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

