Antigen delivered by anthrax lethal toxin induces the development of memory CD8+ T cells that can be rapidly boosted and display effector functions
- PMID: 18086810
- PMCID: PMC2258811
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01208-07
Antigen delivered by anthrax lethal toxin induces the development of memory CD8+ T cells that can be rapidly boosted and display effector functions
Abstract
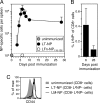
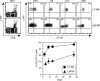
Memory CD8+ T cells are essential for protective immunity against many intracellular pathogens; therefore, stimulation of this population of cells is an important goal of vaccination. We have previously shown that a detoxified derivative of Bacillus anthracis anthrax lethal toxin (LT) can deliver heterologous CD8+ T-cell epitopes to the major histocompatibility complex class I processing and presentation pathway of murine host cells and that immunization of mice with these LT-antigen fusion proteins leads to the induction of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. In this report we extend these findings to include a detailed characterization of the phenotypic and functional properties of the T cells stimulated by the LT-based system. We found that after an initial period of expansion and contraction, antigen-specific CD8+ T cells differentiated into a pool of memory cells that produced gamma interferon and displayed in vivo cytotoxic activity. The transition to memory cells appeared to be quite rapid based on an analysis of the phenotypic marker CD127 and the effectiveness of a booster immunization administered early after the initial immunization. We also investigated the composition of the memory T-cell pool induced by this system and found that while one immunization induced a mixture of effector memory T cells (CD62Llow) and central memory T cells (CD62Lhigh), a second immunization preferentially elevated the effector memory T-cell frequency. Finally, we demonstrated that mice that received prime-boost immunizations of LT-antigen proteins were more protected in a Listeria monocytogenes challenge model than mice that received only one immunization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunization with dendritic cells loaded with alpha-galactosylceramide at priming phase, but not at boosting phase, enhances cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity against infection by intracellular bacteria.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007 Nov;51(2):350-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2007.00316.x. Epub 2007 Aug 29. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17760876
-
Superior protective immunity against murine listeriosis by combined vaccination with CpG DNA and recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2009 Dec;77(12):5501-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00700-09. Epub 2009 Sep 21. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19797070 Free PMC article.
-
Single chain MHC I trimer-based DNA vaccines for protection against Listeria monocytogenes infection.Vaccine. 2012 Mar 9;30(12):2178-86. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.01.012. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Vaccine. 2012. PMID: 22285270 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes: a model pathogen to study antigen-specific memory CD8 T cell responses.Semin Immunopathol. 2015 May;37(3):301-10. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0477-5. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Semin Immunopathol. 2015. PMID: 25860798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sepsis-induced changes in differentiation, maintenance, and function of memory CD8 T cell subsets.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 23;14:1130009. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1130009. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36756117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modular domain swapping among the bacterial cytotoxic necrotizing factor (CNF) family for efficient cargo delivery into mammalian cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 9;293(10):3860-3870. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001381. Epub 2018 Jan 25. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29371399 Free PMC article.
-
Memories that last forever: strategies for optimizing vaccine T-cell memory.Blood. 2010 Mar 4;115(9):1678-89. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-227546. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Blood. 2010. PMID: 19903895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A polymeric protein induces specific cytotoxicity in a TLR4 dependent manner in the absence of adjuvants.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045705. Epub 2012 Sep 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029192 Free PMC article.
-
STxB as an Antigen Delivery Tool for Mucosal Vaccination.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Mar 10;14(3):202. doi: 10.3390/toxins14030202. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35324699 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arora, N., and S. H. Leppla. 1993. Residues 1-254 of anthrax toxin lethal factor are sufficient to cause cellular uptake of fused polypeptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2683334-3341. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann, M. F., P. Wolint, K. Schwarz, P. Jager, and A. Oxenius. 2005. Functional properties and lineage relationship of CD8+ T cell subsets identified by expression of IL-7 receptor alpha and CD62L. J. Immunol. 1754686-4696. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac, V. P., and J. T. Harty. 2007. Manipulating the rate of memory CD8+ T cell generation after acute infection. J. Immunol. 17953-63. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac, V. P., K. A. Messingham, A. Jabbari, J. S. Haring, and J. T. Harty. 2005. Accelerated CD8+ T-cell memory and prime-boost response after dendritic-cell vaccination. Nat. Med. 11748-756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

