Fluid secretion caused by aerolysin-like hemolysin of Aeromonas sobria in the intestines is due to stimulation of production of prostaglandin E2 via cyclooxygenase 2 by intestinal cells
- PMID: 18086811
- PMCID: PMC2258848
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01098-07
Fluid secretion caused by aerolysin-like hemolysin of Aeromonas sobria in the intestines is due to stimulation of production of prostaglandin E2 via cyclooxygenase 2 by intestinal cells
Abstract
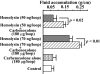
To clarify the mechanisms of diarrheal disease induced by Aeromonas sobria, we examined whether prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) was involved in the intestinal secretory action of A. sobria hemolysin by use of a mouse intestinal loop model. The amount of PGE2 in jejunal fluid and the fluid accumulation ratio were directly related to the dose of hemolysin. The increase over time in the level of PGE2 was similar to that of the accumulated fluid. In addition, hemolysin-induced fluid secretion and PGE2 synthesis were inhibited by the selective cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibitor NS-398 but not the COX-1 inhibitor SC-560. Western blot analysis revealed that hemolysin increased the COX-2 protein levels but reduced the COX-1 protein levels in mouse intestinal mucosa in vivo. These results suggest that PGE2 functions as an important mediator of diarrhea caused by hemolysin and that PGE2 is produced primarily through a COX-2-dependent mechanism. Subsequently, we examined the relationship between PGE2, cyclic AMP (cAMP), and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) Cl- channels in mouse intestinal mucosa exposed to hemolysin. Hemolysin increased the levels of cAMP in the intestinal mucosa. NS-398 inhibited the increase in cAMP production, but SC-560 did not. In addition, H-89, a cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor, and glibenclamide, a CFTR inhibitor, inhibited fluid accumulation. Taken together, these results indicate that hemolysin activates PGE2 production via COX-2 and that PGE2 stimulates cAMP production. cAMP then activates PKA, which in turn stimulates CFTR Cl- channels and finally leads to fluid accumulation in the intestines.
Figures


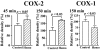


Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E2 induces chloride secretion through crosstalk between cAMP and calcium signaling in mouse inner medullary collecting duct cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 Feb 1;306(3):C263-78. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00381.2012. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24284792 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic tensile force up-regulates BMP-2 expression through MAP kinase and COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathways in human periodontal ligament cells.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Apr 15;323(1):232-241. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.02.013. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24561081
-
A pore-forming toxin produced by Aeromonas sobria activates cAMP-dependent Cl- secretory pathways to cause diarrhea.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005 Jan 15;242(2):195-201. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2004.11.009. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005. PMID: 15621437
-
Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin induces cyclooxygenase-2 and fluid secretion in intestinal epithelial cells through NF-kappaB activation.Eur J Immunol. 2006 Sep;36(9):2446-56. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535808. Eur J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16892182
-
Effect of COX-2 inhibitor NS-398 on expression of PGE2 receptor subtypes in M-1 mouse CCD cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001 Jul;281(1):F123-32. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.2001.281.1.F123. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11399653
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanism of Escherichia coli H10407 induced diarrhoea and its control through immunomodulatory action of bioactives from Simarouba amara (Aubl.).J Microbiol. 2021 Apr;59(4):435-447. doi: 10.1007/s12275-021-0423-2. Epub 2021 Feb 25. J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33630248
References
-
- Beubler, E., R. Schuligoi, A. K. Chopra, D. A. Ribardo, and B. A. Peskar. 2001. Cholera toxin induces prostaglandin synthesis via post-transcriptional activation of cyclooxygenase-2 in the rat jejunum. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 297940-945. - PubMed
-
- Breyer, R. M., L. S. Davis, C. Nian, R. Redha, B. Stillman, H. R. Jacobson, and M. D. Breyer. 1996. Cloning and expression of the rabbit prostaglandin EP4 receptor. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol. 270F485-F493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

