Sensing gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharides: a human disease determinant?
- PMID: 18086818
- PMCID: PMC2223455
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00939-07
Sensing gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharides: a human disease determinant?
Figures
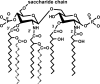
References
-
- Abreu, M. T., M. Fukata, and M. Arditi. 2005. TLR signaling in the gut in health and disease. J. Immunol. 1744453-4460. - PubMed
-
- Adamo, R., S. Sokol, G. Soong, M. I. Gomez, and A. Prince. 2004. Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagella activate airway epithelial cells through asialoGM1 and Toll-like receptor 2 as well as Toll-like receptor 5. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 30627-634. - PubMed
-
- Aisenberg, G., K. V. Rolston, B. F. Dickey, D. P. Kontoyiannis, I. I. Raad, and A. Safdar. 2007. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia pneumonia in cancer patients without traditional risk factors for infection, 1997-2004. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2613-20. - PubMed
-
- Arditi, M., L. Ables, and R. Yogev. 1989. Cerebrospinal fluid endotoxin levels in children with H. influenzae meningitis before and after administration of intravenous ceftriaxone. J. Infect. Dis. 1601005-1011. - PubMed
-
- Backhed, F., and M. Hornef. 2003. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated signaling by epithelial surfaces: necessity or threat? Microb. Infect. 5951-959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

