Induction of erm(C) expression by noninducing antibiotics
- PMID: 18086834
- PMCID: PMC2258491
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01266-07
Induction of erm(C) expression by noninducing antibiotics
Abstract
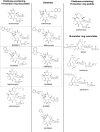
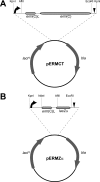
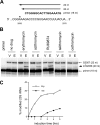
Ketolides, which represent the newest macrolide antibiotics, are generally perceived to be noninducers of inducible erm genes. In the study described in this paper we investigated the effects of several macrolide and ketolide compounds on the expression of the inducible erm(C) gene by Escherichia coli cells. Exposure to 14-member-ring macrolide drugs and to azithromycin led to a rapid and pronounced increase in the extent of dimethylation of Erm(C) target residue A2058 in 23S rRNA. When cells were incubated with subinhibitory concentrations of ketolides, the extent of A2058 dimethylation was also increased, albeit to a lower level and with kinetics slower than those observed with macrolides. The induction of erm(C) expression by ketolides was further confirmed by using a reporter construct which allows the colorimetric detection of induction in a disc diffusion assay. Most of the ketolides tested, including the clinically relevant compounds telithromycin and cethromycin, were able to induce the reporter expression, even though the induction occurred within a more narrow range of concentrations compared to the concentration range at which induction was achieved with the inducing macrolide antibiotics. No induction of the reporter expression was observed with 16-member-ring macrolide antibiotics or with a control drug, chloramphenicol. The deletion of three codons of the erm(C) leader peptide eliminated macrolide-dependent induction but left ketolide-dependent induction unchanged. We conclude that ketolides are generally capable of inducing erm genes. The narrow range of ketolide inducing concentrations, coupled with the slow rate of induction and the lower steady-state level of ribosome methylation, may mask this effect in MIC assays.
Figures



References
-
- Bonnefoy, A., A. M. Girard, C. Agouridas, and J. F. Chantot. 1997. Ketolides lack inducibility properties of MLS(B) resistance phenotype. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 40:85-90. - PubMed
-
- Bryskier, A. 2000. Ketolides—telithromycin, an example of a new class of antibacterial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 6:661-669. - PubMed
-
- Champney, W. S., H. S. Chittum, and C. L. Tober. 2003. A 50S ribosomal subunit precursor particle is a substrate for the ermC methyltransferase in Staphylococcus aureus cells. Curr. Microbiol. 46:453-460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

