Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide-mediated up-regulation of beta-cell antiapoptotic Bcl-2 gene expression is coordinated by cyclic AMP (cAMP) response element binding protein (CREB) and cAMP-responsive CREB coactivator 2
- PMID: 18086876
- PMCID: PMC2258787
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00325-07
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide-mediated up-regulation of beta-cell antiapoptotic Bcl-2 gene expression is coordinated by cyclic AMP (cAMP) response element binding protein (CREB) and cAMP-responsive CREB coactivator 2
Abstract
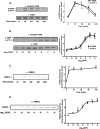
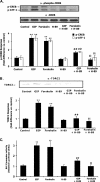
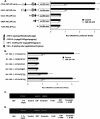
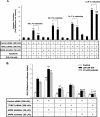
The cyclic AMP (cAMP)/protein kinase A (PKA) cascade plays a central role in beta-cell proliferation and apoptosis. Here, we show that the incretin hormone glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) stimulates expression of the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 gene in pancreatic beta cells through a pathway involving AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), cAMP-responsive CREB coactivator 2 (TORC2), and cAMP response element binding protein (CREB). Stimulation of beta-INS-1 (clone 832/13) cells with GIP resulted in increased Bcl-2 promoter activity. Analysis of the rat Bcl-2 promoter revealed two potential cAMP response elements, one of which (CRE-I [GTGACGTAC]) was shown, using mutagenesis and deletion analysis, to be functional. Subsequent studies established that GIP increased the nuclear localization of TORC2 and phosphorylation of CREB serine 133 through a pathway involving PKA activation and reduced AMPK phosphorylation. At the nuclear level, phospho-CREB and TORC2 were demonstrated to bind to CRE-I of the Bcl-2 promoter, and GIP treatment resulted in increases in their interaction. Furthermore, GIP-mediated cytoprotection was partially reversed by small interfering RNA-mediated reduction in BCL-2 or TORC2/CREB or by pharmacological activation of AMPK. The antiapoptotic effect of GIP in beta cells is therefore partially mediated through a novel mode of transcriptional regulation of Bcl-2 involving cAMP/PKA/AMPK-dependent regulation of CREB/TORC2 activity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
GIP increases human adipocyte LPL expression through CREB and TORC2-mediated trans-activation of the LPL gene.J Lipid Res. 2010 Nov;51(11):3145-57. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M006841. Epub 2010 Aug 7. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20693566 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) stimulation of pancreatic beta-cell survival is dependent upon phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB) signaling, inactivation of the forkhead transcription factor Foxo1, and down-regulation of bax expression.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 10;280(23):22297-307. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500540200. Epub 2005 Apr 6. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15817464
-
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 modulate beta-cell chromatin structure.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 8;284(19):12896-904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809046200. Epub 2009 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19279000 Free PMC article.
-
Roles and regulation of the transcription factor CREB in pancreatic β -cells.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Nov;4(3):187-95. doi: 10.2174/1874467211104030187. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21488836 Review.
-
Regulation of somatostatin gene transcription by cyclic adenosine monophosphate.Metabolism. 1996 Aug;45(8 Suppl 1):4-7. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(96)90068-2. Metabolism. 1996. PMID: 8769368 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Peptide Prevents Serum Deprivation-Induced Apoptosis in Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Osteoblastic Cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015 Dec;11(6):841-51. doi: 10.1007/s12015-015-9616-6. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015. PMID: 26254594
-
Transcriptional analysis of apoptotic cerebellar granule neurons following rescue by gastric inhibitory polypeptide.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 1;15(4):5596-622. doi: 10.3390/ijms15045596. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24694544 Free PMC article.
-
Sitagliptin (MK0431) inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV decreases nonobese diabetic mouse CD4+ T-cell migration through incretin-dependent and -independent pathways.Diabetes. 2010 Jul;59(7):1739-50. doi: 10.2337/db09-1618. Epub 2010 Apr 5. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20368408 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of baicalein analogs with modification of the 6th position of A ring on the activity toward NF-kappaB-, AP-1-, or CREB-mediated transcription.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Sep 15;18(18):5046-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.08.001. Epub 2008 Aug 6. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008. PMID: 18722769 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary miR-16 transactivated by C/EBPβ reduces kidney function after ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 14;6:27945. doi: 10.1038/srep27945. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27297958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonner-Weir, S. 2001. Beta-cell turnover: its assessment and implications. Diabetes 50(Suppl. 1)S20-S24. - PubMed
-
- Bonner-Weir, S., D. Deery, J. L. Leahy, and G. C. Weir. 1989. Compensatory growth of pancreatic beta-cells in adult rats after short-term glucose infusion. Diabetes 3849-53. - PubMed
-
- Brelje, T. C., J. A. Parsons, and R. L. Sorenson. 1994. Regulation of islet beta-cell proliferation by prolactin in rat islets. Diabetes 43263-273. - PubMed
-
- Buteau, J., W. El-Assaad, C. J. Rhodes, L. Rosenberg, E. Joly, and M. Prentki. 2004. Glucagon-like peptide-1 prevents beta cell glucolipotoxicity. Diabetologia 47806-815. - PubMed
-
- Butler, A. E., J. Janson, S. Bonner-Weir, R. Ritzel, R. A. Rizza, and P. C. Butler. 2003. β-Cell deficit and increased β-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52102-110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
