ARS2 is a conserved eukaryotic gene essential for early mammalian development
- PMID: 18086880
- PMCID: PMC2258792
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01565-07
ARS2 is a conserved eukaryotic gene essential for early mammalian development
Abstract
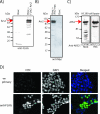
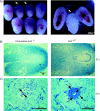
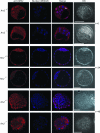
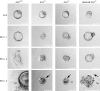
Determining the functions of novel genes implicated in cell survival is directly relevant to our understanding of mammalian development and carcinogenesis. ARS2 is an evolutionarily conserved gene that confers arsenite resistance on arsenite-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary cells. Little is known regarding the function of ARS2 in mammals. We report that ARS2 is transcribed throughout embryonic development and is expressed ubiquitously in mouse and human tissues. The mouse ARS2 protein is predominantly localized to the nucleus, and this nuclear localization is ablated in ARS2-null embryos, which in turn die around the time of implantation. After 24 h of culture, ARS2-null blastocysts contained a significantly greater number of apoptotic cells than wild-type or heterozygous blastocysts. By 48 h of in vitro culture, null blastocysts invariably collapsed and failed to proliferate. These data indicate ARS2 is essential for early mammalian development and is likely involved in an essential cellular process. The analysis of data from several independent protein-protein interaction studies in mammals, combined with functional studies of its Arabidopsis ortholog, SERRATE, suggests that this essential process is related to RNA metabolism.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Taube nuss is a novel gene essential for the survival of pluripotent cells of early mouse embryos.Development. 2000 Dec;127(24):5449-61. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.24.5449. Development. 2000. PMID: 11076765
-
Mutagenesis of ARS2 Domains To Assess Possible Roles in Cell Cycle Progression and MicroRNA and Replication-Dependent Histone mRNA Biogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Nov;35(21):3753-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00272-15. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26303529 Free PMC article.
-
Gene structure and embryonic expression of mouse COP9 signalosome subunit 8 (Csn8).Gene. 2003 Dec 4;321:65-72. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(03)00836-9. Gene. 2003. PMID: 14636993
-
ARS2/SRRT: at the nexus of RNA polymerase II transcription, transcript maturation and quality control.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Jun 30;49(3):1325-1336. doi: 10.1042/BST20201008. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34060620 Review.
-
Arsenic resistance protein 2 and microRNA biogenesis: Biological implications in cancer development.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Apr;244:108386. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108386. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36933704 Review.
Cited by
-
Ars2 regulates both miRNA- and siRNA- dependent silencing and suppresses RNA virus infection in Drosophila.Cell. 2009 Jul 23;138(2):340-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.045. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19632183 Free PMC article.
-
Microprocessor of microRNAs: regulation and potential for therapeutic intervention.Mol Cancer. 2010 Jun 1;9:134. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-134. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20515486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis RNA processing factor SERRATE regulates the transcription of intronless genes.Elife. 2018 Aug 28;7:e37078. doi: 10.7554/eLife.37078. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30152752 Free PMC article.
-
Ars2 links the nuclear cap-binding complex to RNA interference and cell proliferation.Cell. 2009 Jul 23;138(2):328-39. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.046. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19632182 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic switch of ARS2 isoforms promotes nonsense-mediated mRNA decay and arsenic sensitivity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Feb 22;50(3):1620-1638. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac033. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35104878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clarke, J. H., D. Tack, K. Findlay, M. Van Montagu, and M. Van Lijsebettens. 1999. The SERRATE locus controls the formation of the early juvenile leaves and phase length in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 20493-501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
