Phosphorylation by casein kinase 2 regulates Nap1 localization and function
- PMID: 18086883
- PMCID: PMC2258750
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01035-07
Phosphorylation by casein kinase 2 regulates Nap1 localization and function
Abstract
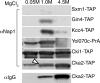
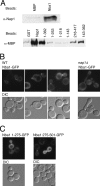
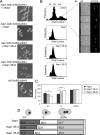
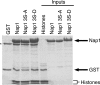
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the evolutionarily conserved nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein Nap1 is a cofactor for the import of histones H2A and H2B, a chromatin assembly factor and a mitotic factor involved in regulation of bud formation. To understand the mechanism by which Nap1 function is regulated, Nap1-interacting factors were isolated and identified by mass spectrometry. We identified several kinases among these proteins, including casein kinase 2 (CK2), and a new bud neck-associated protein, Nba1. Consistent with our identification of the Nap1-interacting kinases, we showed that Nap1 is phosphorylated in vivo at 11 sites and that Nap1 is phosphorylated by CK2 at three substrate serines. Phosphorylation of these serines was not necessary for normal bud formation, but mutation of these serines to either alanine or aspartic acid resulted in cell cycle changes, including a prolonged S phase, suggesting that reversible phosphorylation by CK2 is important for cell cycle regulation. Nap1 can shuttle between the nucleus and cytoplasm, and we also showed that CK2 phosphorylation promotes the import of Nap1 into the nucleus. In conclusion, our data show that Nap1 phosphorylation by CK2 appears to regulate Nap1 localization and is required for normal progression through S phase.
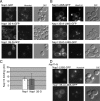
Figures


References
-
- Adachi, Y., G. N. Pavlakis, and T. D. Copeland. 1994. Identification and characterization of SET, a nuclear phosphoprotein encoded by the translocation break point in acute undifferentiated leukemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2692258-2262. - PubMed
-
- Adachi, Y., G. N. Pavlakis, and T. D. Copeland. 1994. Identification of in vivo phosphorylation sites of SET, a nuclear phosphoprotein encoded by the translocation breakpoint in acute undifferentiated leukemia. FEBS Lett. 340231-235. - PubMed
-
- Aitchison, J. D., M. P. Rout, M. Marelli, G. Blobel, and R. W. Wozniak. 1995. Two novel related yeast nucleoporins Nup170p and Nup157p: complementation with the vertebrate homologue Nup155p and functional interactions with the yeast nuclear pore-membrane protein Pom152p. J. Cell Biol. 1311133-1148. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akada, R., J. Yamamoto, and I. Yamashita. 1997. Screening and identification of yeast sequences that cause growth inhibition when overexpressed. Mol. Gen. Genet. 254267-274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
