Regulation of neuron-specific alternative splicing of neurofibromatosis type 1 pre-mRNA
- PMID: 18086893
- PMCID: PMC2258745
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01509-07
Regulation of neuron-specific alternative splicing of neurofibromatosis type 1 pre-mRNA
Abstract
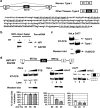
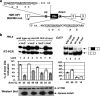
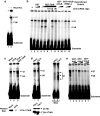
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is one of the most common heritable autosomal dominant disorders. Alternative splicing modulates the function of neurofibromin, the NF1 gene product, by inserting the in-frame exon 23a into the region of NF1 mRNA that encodes the GTPase-activating protein-related domain. This insertion, which is predominantly skipped in neurons, reduces the ability of neurofibromin to regulate Ras by 10-fold. Here, we report that the neuron-specific Hu proteins control the production of the short protein isoform by suppressing inclusion of NF1 exon 23a, while TIA-1/TIAR proteins promote inclusion of this exon. We identify two binding sites for Hu proteins, located upstream and downstream of the regulated exon, and provide biochemical evidence that Hu proteins specifically block exon definition by preventing binding of essential splicing factors. In vitro analyses using nuclear extracts show that at the downstream site, Hu proteins prevent binding of U1 and U6 snRNPs to the 5' splice site, while TIAR increases binding. Hu proteins also decrease U2AF binding at the 3' splice site located upstream of exon 23a. In addition to providing the first mechanistic insight into tissue-specific control of NF1 splicing, these studies establish a novel strategy whereby Hu proteins regulate RNA processing.
Figures





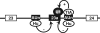
Similar articles
-
The neurofibromatosis type I pre-mRNA is a novel target of CELF protein-mediated splicing regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(1):253-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp766. Epub 2009 Oct 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19854948 Free PMC article.
-
Hu antigen R (HuR) functions as an alternative pre-mRNA splicing regulator of Fas apoptosis-promoting receptor on exon definition.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 4;283(27):19077-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800017200. Epub 2008 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18463097
-
Alternative splicing of the neurofibromatosis type I pre-mRNA.Biosci Rep. 2012 Apr 1;32(2):131-8. doi: 10.1042/BSR20110060. Biosci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22115364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative splicing of the neurofibromatosis type 1 pre-mRNA is regulated by the muscleblind-like proteins and the CUG-BP and ELAV-like factors.BMC Mol Biol. 2012 Dec 10;13:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-13-35. BMC Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23227900 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Splicing of Exon 23a in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Pre-mRNA: Its Contribution to the Protein Structure and Function of Neurofibromin.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2025 Jul-Aug;16(4):e70021. doi: 10.1002/wrna.70021. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2025. PMID: 40812791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA protein interaction in neurons.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2013 Jul 8;36:243-70. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062912-114322. Epub 2013 May 20. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23701460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Situ Peroxidase Labeling Followed by Mass-Spectrometry Reveals TIA1 Interactome.Biology (Basel). 2022 Feb 11;11(2):287. doi: 10.3390/biology11020287. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205152 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular localization and interaction of mRNA binding proteins as detected by FRET.BMC Cell Biol. 2010 Sep 15;11:69. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-11-69. BMC Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20843363 Free PMC article.
-
Elavl3 is essential for the maintenance of Purkinje neuron axons.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 9;8(1):2722. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21130-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29426875 Free PMC article.
-
Three RNA recognition motifs participate in RNA recognition and structural organization by the pro-apoptotic factor TIA-1.J Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 27;415(4):727-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.040. Epub 2011 Dec 2. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22154808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akamatsu, W., H. Fujihara, T. Mitsuhashi, M. Yano, S. Shibata, Y. Hayakawa, H. J. Okano, S. Sakakibara, H. Takano, T. Takano, T. Takahashi, T. Noda, and H. Okano. 2005. The RNA-binding protein HuD regulates neuronal cell identity and maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1024625-4630. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akamatsu, W., H. J. Okano, N. Osumi, T. Inoue, S. Nakamura, S. Sakakibara, M. Miura, N. Matsuo, R. B. Darnell, and H. Okano. 1999. Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 969885-9890. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen, L. B., R. Ballester, D. A. Marchuk, E. Chang, D. H. Gutmann, A. M. Saulino, J. Camonis, M. Wigler, and F. S. Collins. 1993. A conserved alternative splice in the von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis (NF1) gene produces two neurofibromin isoforms, both of which have GTPase-activating protein activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13487-495. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
