A molecular specificity code for the three mammalian KDEL receptors
- PMID: 18086916
- PMCID: PMC2140024
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200705180
A molecular specificity code for the three mammalian KDEL receptors
Erratum in
- J Cell Biol. 2008 Feb 11;180(3):645
Abstract
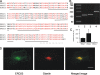
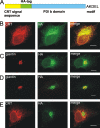
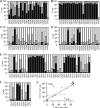
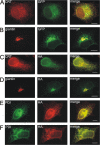
AC-terminal KDEL-like motif prevents secretion of soluble endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident proteins. This motif interacts with KDEL receptors localized in the intermediate compartment and Golgi apparatus. Such binding triggers retrieval back to the ER via a coat protein I-dependent pathway. To date, two human KDEL receptors have been reported. Here, we report the Golgi localization of a third human KDEL receptor. Using a reporter construct system from a screen of 152 variants, we identified 35 KDEL-like variants that result in efficient ER localization but do not match the current Prosite motif for ER localization ([KRHQSA]-[DENQ]-E-L). We cloned 16 human proteins with one of these motifs and all were found in the ER. A subsequent screen by bimolecular fluorescence complementation determined the specificities of the three human KDEL receptors. Each KDEL receptor has a unique pattern of motifs with which it interacts. This suggests a specificity in the retrieval of human proteins that contain different KDEL variants.
Figures

References
-
- Alanen, H.I., K.E.H. Salo, M. Pekkala, H.M. Siekkinen, A. Pirneskoski, and L.W. Ruddock. 2003. a. Defining the domain boundaries of the human protein disulphide isomerases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 5:367–377. - PubMed
-
- Alanen, H.I., R.A. Williamson, M.J. Howard, A.-K. Lappi, H.P. Jäntti, S.M. Rautio, S. Kellokumpu, and L.W. Ruddock. 2003. b. Functional characterization of ERp18, a new endoplasmic reticulum-located thioredoxin superfamily member. J. Biol. Chem. 278:28912–28920. - PubMed
-
- Alanen, H.I., R.A. Williamson, M.J. Howard, F.S. Hatahet, K.E.H. Salo, A. Kauppila, S. Kellokumpu, and L.W. Ruddock. 2006. ERp27, a new non-catalytic endoplasmic reticulum-located human protein disulfide isomerase family member, interacts with ERp57. J. Biol. Chem. 281:33727–33738. - PubMed
-
- Anson, D.S., and J. Bielicki. 1999. Sulphamidase. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 31:363–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

