Newly identified biologically active and proteolysis-resistant VEGF-A isoform VEGF111 is induced by genotoxic agents
- PMID: 18086921
- PMCID: PMC2140032
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200703052
Newly identified biologically active and proteolysis-resistant VEGF-A isoform VEGF111 is induced by genotoxic agents
Abstract
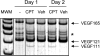
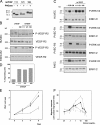
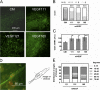
Ultraviolet B and genotoxic drugs induce the expression of a vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) splice variant (VEGF111) encoded by exons 1-4 and 8 in many cultured cells. Although not detected in a series of normal human and mouse tissue, VEGF111 expression is induced in MCF-7 xenografts in nude mice upon treatment by camptothecin. The skipping of exons that contain proteolytic cleavage sites and extracellular matrix-binding domains makes VEGF111 diffusible and resistant to proteolysis. Recombinant VEGF111 activates VEGF receptor 2 (VEGF-R2) and extracellularly regulated kinase 1/2 in human umbilical vascular endothelial cells and porcine aortic endothelial cells expressing VEGF-R2. The mitogenic and chemotactic activity and VEGF111's ability to promote vascular network formation during embyonic stem cell differentiation are similar to those of VEGF121 and 165. Tumors in nude mice formed by HEK293 cells expressing VEGF111 develop a more widespread network of numerous small vessels in the peritumoral tissue than those expressing other isoforms. Its potent angiogenic activity and remarkable resistance to proteolysis makes VEGF111 a potential adverse factor during chemotherapy but a beneficial therapeutic tool for ischemic diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Bates, D.O., T.G. Cui, J.M. Doughty, M. Winkler, M. Sugiono, J.D. Shields, D. Peat, D. Gillatt, and S.J. Harper. 2002. VEGF165b, an inhibitory splice variant of vascular endothelial growth factor, is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 62:4123–4131. - PubMed
-
- Blaudschun, R., C. Sunderkotter, P. Brenneisen, R. Hinrichs, T. Peters, L. Schneider, Z. Razi-Wolf, N. Hunzelmann, and K. Scharffetter-Kochanek. 2002. Vascular endothelial growth factor causally contributes to the angiogenic response upon ultraviolet B irradiation in vivo. Br. J. Dermatol. 146:581–587. - PubMed
-
- Burchardt, M., T. Burchardt, A.G. Anastasiadis, R. Buttyan, A. de la Taille, A. Shabsigh, J. Frank, and R. Shabsigh. 2005. Application of angiogenic factors for therapy of erectile dysfunction: protein and DNA transfer of VEGF 165 into the rat penis. Urology. 66:665–670. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell, R.B., M. Bartoli, M.A. Behzadian, A.E. El-Remessy, M. Al-Shabrawey, D.H. Platt, G.I. Liou, and R.W. Caldwell. 2005. Vascular endothelial growth factor and diabetic retinopathy: role of oxidative stress. Curr. Drug Targets. 6:511–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

