Structural basis for the high all-trans-retinaldehyde reductase activity of the tumor marker AKR1B10
- PMID: 18087047
- PMCID: PMC2410076
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705659105
Structural basis for the high all-trans-retinaldehyde reductase activity of the tumor marker AKR1B10
Abstract
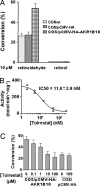
AKR1B10 is a human aldo-keto reductase (AKR) found to be elevated in several cancer types and in precancerous lesions. In vitro, AKR1B10 exhibits a much higher retinaldehyde reductase activity than any other human AKR, including AKR1B1 (aldose reductase). We here demonstrate that AKR1B10 also acts as a retinaldehyde reductase in vivo. This activity may be relevant in controlling the first step of retinoic acid synthesis. Up-regulation of AKR1B10, resulting in retinoic acid depletion, may lead to cellular proliferation. Both in vitro and in vivo activities of AKR1B10 were inhibited by tolrestat, an AKR1B1 inhibitor developed for diabetes treatment. The crystal structure of the ternary complex AKR1B10-NADP(+)-tolrestat was determined at 1.25-A resolution. Molecular dynamics models of AKR1B10 and AKR1B1 with retinaldehyde isomers and site-directed mutagenesis show that subtle differences at the entrance of the retinoid-binding site, especially at position 125, are determinant for the all-trans-retinaldehyde specificity of AKR1B10. Substitutions in the retinaldehyde cyclohexene ring also influence the specificity. These structural features should facilitate the design of specific inhibitors, with potential use in cancer and diabetes treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


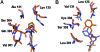
Similar articles
-
Human and rodent aldo-keto reductases from the AKR1B subfamily and their specificity with retinaldehyde.Chem Biol Interact. 2011 May 30;191(1-3):199-205. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2011.02.007. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Chem Biol Interact. 2011. PMID: 21329680 Free PMC article.
-
Aldo-keto reductases from the AKR1B subfamily: retinoid specificity and control of cellular retinoic acid levels.Chem Biol Interact. 2009 Mar 16;178(1-3):171-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2008.10.027. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Chem Biol Interact. 2009. PMID: 19014918
-
X-ray structure of the V301L aldo-keto reductase 1B10 complexed with NADP(+) and the potent aldose reductase inhibitor fidarestat: implications for inhibitor binding and selectivity.Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Feb 25;202(1-3):178-85. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2012.12.013. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Chem Biol Interact. 2013. PMID: 23295227
-
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B1 inhibitors: old drugs with new perspectives.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2009 Nov;4(3):246-53. doi: 10.2174/157489209789206931. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2009. PMID: 19522700 Review.
-
All in the family: aldose reductase and closely related aldo-keto reductases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Apr;61(7-8):737-49. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3402-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15094999 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota-mitochondrial inter-talk in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 20;9:934113. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.934113. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36204383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiomics characterization of fatty acid metabolism for the clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 18;13(1):22472. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50156-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38110715 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of AKR1B10 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Apr 5;11(4):486. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040486. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30959792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AKR1B10 activates diacylglycerol (DAG) second messenger in breast cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2018 Oct;57(10):1300-1310. doi: 10.1002/mc.22844. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Mol Carcinog. 2018. PMID: 29846015 Free PMC article.
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver secretome.Arch Pharm Res. 2022 Dec;45(12):938-963. doi: 10.1007/s12272-022-01419-w. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Arch Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 36441472 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cao D, Fan ST, Chung SS. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:11429–11435. - PubMed
-
- Hyndman DJ, Flynn TG. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1399:198–202. - PubMed
-
- Scuric Z, Stain SC, Anderson WF, Hwang JJ. Hepatology. 1998;27:943–950. - PubMed
-
- Fukumoto S, Yamauchi N, Moriguchi H, Hippo Y, Watanabe A, Shibahara J, Taniguchi H, Ishikawa S, Ito H, Yamamoto S, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:1776–1785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

