The GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 18088381
- PMCID: PMC3073119
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05194.x
The GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
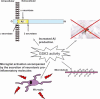
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) is a constitutively active, proline-directed serine/threonine kinase that plays a part in a number of physiological processes ranging from glycogen metabolism to gene transcription. GSK3 also plays a pivotal and central role in the pathogenesis of both sporadic and familial forms of Alzheimer's disease (AD), an observation that has led us to coin the 'GSK3 hypothesis of AD'. According to this hypothesis, over-activity of GSK3 accounts for memory impairment, tau hyper-phosphorylation, increased beta-amyloid production and local plaque-associated microglial-mediated inflammatory responses; all of which are hallmark characteristics of AD. If our 'GSK3 hypothesis of AD' is substantiated and GSK3 is indeed a causal mediator of AD then inhibitors of GSK3 would provide a novel avenue for therapeutic intervention in this devastating disorder.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez G, Munoz-Montano JR, Satrustegui J, Avila J, Bogonez E, az-Nido J. Lithium protects cultured neurons against beta-amyloid-induced neurodegeneration. FEBS Lett. 1999;453:260–264. - PubMed
-
- Anderton BH, Betts J, Blackstock WP, et al. Sites of phosphorylation in tau and factors affecting their regulation. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 2001;67:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Asuni AA, Hooper C, Reynolds CH, Lovestone S, Anderton BH, Killick R. GSK3alpha exhibits beta-catenin and tau directed kinase activities that are modulated by Wnt. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006;24:3387–3392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

