Functional analysis of human cytomegalovirus pUS28 mutants in infected cells
- PMID: 18089733
- PMCID: PMC2662737
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.83226-0
Functional analysis of human cytomegalovirus pUS28 mutants in infected cells
Abstract
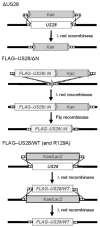
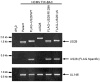
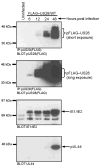
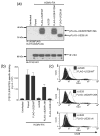
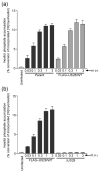
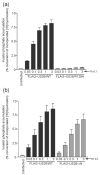
The human cytomegalovirus (HCMV)-encoded viral G protein-coupled receptor pUS28 contributes to an array of biological effects, including cell migration and proliferation. Using FIX-BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome, derived from the HCMV clinical isolate VR1814) and lambda red recombination techniques, we generated HCMV recombinants expressing amino-terminally FLAG-tagged versions of wild-type pUS28 (FLAG-US28/WT), G-protein coupling deficient pUS28 (FLAG-US28/R129A) and chemokine-binding domain deficient pUS28 (FLAG-US28/DeltaN). Infection with the FLAG-US28/R129A virus failed to induce inositol phosphate accumulation, indicating that G-protein coupling is essential for pUS28 signalling to phospholipase C-beta (PLC-beta) during HCMV infection. The FLAG-US28/DeltaN virus induced about 80 % of the level of PLC-beta signalling induced by the FLAG-US28/WT virus, demonstrating that the N-terminal chemokine-binding domain is not required for pUS28-induced PLC-beta signalling in infected cells. The data presented here are the first to describe the functional analyses of several key pUS28 mutants in HCMV-infected cells. Elucidating the mechanisms by which pUS28 signals during infection will provide important insights into HCMV pathogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Bennett TA, Maestas DC, Prossnitz ER. Arrestin binding to the G protein-coupled N-formyl peptide receptor is regulated by the conserved “DRY” sequence. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:24590–24594. - PubMed
-
- Bodaghi B, Jones TR, Zipeto D, Vita C, Sun L, Laurent L, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Virelizier JL, Michelson S. Chemokine sequestration by viral chemoreceptors as a novel viral escape strategy: withdrawal of chemokines from the environment of cytomegalovirus-infected cells. J Exp Med. 1998;188:855–866. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boomker JM, Verschuuren EA, Brinker MG, de Leij LF, The TH, Harmsen MC. Kinetics of US28 gene expression during active human cytomegalovirus infection in lung-transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:1552–1556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

