Plasma UGRP1 levels associate with promoter G-112A polymorphism and the severity of asthma
- PMID: 18089940
- PMCID: PMC2768603
- DOI: 10.2332/allergolint.O-07-493
Plasma UGRP1 levels associate with promoter G-112A polymorphism and the severity of asthma
Abstract
Background: Uteroglobin-related protein 1 (UGRP1) is a secretory protein expressed in the airways and is speculated to have anti-inflammatory activity. In the mouse, its gene expression is down-regulated by interleukin (IL)-5 and -9, and up-regulated by IL-10. However, the precise role of UGRP1 in human inflammatory airway diseases such as asthma has not been clarified. The objectives of this study were to establish an ELISA system to quantify UGRP1 protein, and to examine whether plasma UGRP1 levels are associated with the G-112A polymorphism, asthma susceptibility, and its severity.
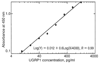
Methods: 152 asthma patients and 103 normal controls were involved in this study. Mice were immunized with recombinant UGRP1 and hybridoma cell lines were established. A sandwich ELISA system was established by using two monoclonal antibodies recognizing different epitopes. Plasma UGRP1 levels were measured with the ELISA system and the G-112A allele was detected by using real-time PCR.
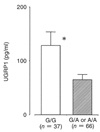
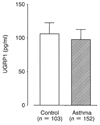
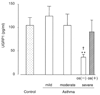
Results: An ELISA system was established that allowed determination of UGRP1 levels within the range of 9.6-1250 pg/ml. The mean plasma UGRP1 levels for subjects with -112A allele were significantly lower than those without it (p = 0.025). Although there was no significant difference in the plasma UGRP1 levels between asthma patients and controls (p = 0.13), severe asthma patients without oral corticosteroid had significantly lower plasma UGRP1 levels compared to mild- or moderate- asthma patients and controls (p = 0.004, 0.03 and 0.003, respectively).
Conclusions: The ELISA system for quantifying UGRP1 protein was established, and plasma UGRP1 levels were associated with the G-112A UGRP1 gene promoter polymorphism and the severity of asthma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The -112G>A polymorphism of the secretoglobin 3A2 (SCGB3A2) gene encoding uteroglobin-related protein 1 (UGRP1) increases risk for the development of Graves' disease in subsets of patients with elevated levels of immunoglobulin E.J Appl Genet. 2011 May;52(2):201-7. doi: 10.1007/s13353-010-0022-0. Epub 2010 Dec 18. J Appl Genet. 2011. PMID: 21170691
-
Uteroglobulin-related protein 1 and severity of respiratory syncytial virus infection in children admitted to hospital.J Med Virol. 2011 Jun;83(6):1086-92. doi: 10.1002/jmv.22073. J Med Virol. 2011. PMID: 21503925
-
Uteroglobin-related protein 1(UGRP1) gene polymorphisms and atopic asthma in the Indian population.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005 Jan;136(1):1-6. doi: 10.1159/000082578. Epub 2004 Dec 8. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15591807
-
Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Clara cell 10-kDa protein: in pursuit of clinical significance of sera in patients with asthma and sarcoidosis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;923:268-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05535.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 11193763 Review.
-
Interleukin-10 promoter 1082/-819/-592 polymorphisms are associated with asthma susceptibility in Asians and atopic asthma: a meta-analysis.Lung. 2014 Feb;192(1):65-73. doi: 10.1007/s00408-013-9519-8. Epub 2013 Oct 27. Lung. 2014. PMID: 24162871 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic and Genetic predictors and risk scores of cardiovascular diseases in persons living with HIV.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 13:2025.05.08.25327219. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.08.25327219. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40463557 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The -112G>A polymorphism of the secretoglobin 3A2 (SCGB3A2) gene encoding uteroglobin-related protein 1 (UGRP1) increases risk for the development of Graves' disease in subsets of patients with elevated levels of immunoglobulin E.J Appl Genet. 2011 May;52(2):201-7. doi: 10.1007/s13353-010-0022-0. Epub 2010 Dec 18. J Appl Genet. 2011. PMID: 21170691
-
Secretoglobin 3A2 suppresses bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by transforming growth factor beta signaling down-regulation.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 3;286(22):19682-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.239046. Epub 2011 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21478551 Free PMC article.
-
Admixture mapping of severe asthma exacerbations in Hispanic/Latino children and youth.Thorax. 2023 Mar;78(3):233-241. doi: 10.1136/thorax-2022-218755. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Thorax. 2023. PMID: 36180068 Free PMC article.
-
The cytokine-driven regulation of secretoglobins in normal human upper airway and their expression, particularly that of uteroglobin-related protein 1, in chronic rhinosinusitis.Respir Res. 2011 Mar 8;12(1):28. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-28. Respir Res. 2011. PMID: 21385388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niimi T, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, et al. Cloning, expression, and chromosomal localization of the mouse gene (Scgb3a1, alias Ugrp2) that encodes a member of the novel uteroglobin-related protein gene family. Cytogenet. Genome. Res. 2002;97:120–127. - PubMed
-
- Niimi T, Keek-Waggoner CL, Popescu NC, et al. UGRP1, a uteroglobin/Clara cell secretory protein-related protein, is a novel lung-enriched downstream target gene for the T/EBP/NKX2.1 homeodomain transcription factor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001;15:2021–2036. - PubMed
-
- Bohinski RJ, Di Lauro R, Whitsett JA. The lung-specific surfactant protein B gene promoter is a target for thyroid transcription factor 1 and hepatocyte nuclear factor 3, indicating common factors for organ-specific gene expression along the foregut axis. Mol. Cell Biol. 1994;14:5671–5681. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruno MD, Bohinski RJ, Huelsman KM, Whitsett JA, Korfhagen TR. Lung cell-specific expression of the murine surfactant protein A (SP-A) gene is mediated by interactions between the SP-A promoter and thyroid transcription factor-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:6531–6536. - PubMed
-
- Kelly SE, Bachurski CJ, Burhans MS, Glasser SW. Transcription of the lung-specific surfactant protein C gene is mediated by thyroid transcription factor 1. J Biol. Chem. 1996;271:6881–6888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

