Amnion-derived multipotent progenitor cells increase gain of incisional breaking strength and decrease incidence and severity of acute wound failure
- PMID: 18091982
- PMCID: PMC2064968
Amnion-derived multipotent progenitor cells increase gain of incisional breaking strength and decrease incidence and severity of acute wound failure
Abstract
Objective: Acute wound failure is a common complication following surgical procedures and trauma. Laparotomy wound failure leads to abdominal dehiscence and incisional hernia formation. Delayed recovery of wound-breaking strength is one mechanism for laparotomy wound failure. Early fascial wounds are relatively acellular, and there is a delay in the appearance of acute wound growth factors and cytokines. The objective of this study was to accelerate and improve laparotomy wound healing using amnion-derived multipotent cells (AMPs). AMPs' nonimmunogenic phenotype and relative abundance support its role as a cell therapy.
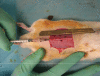
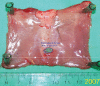
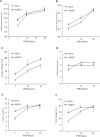
Methods: AMPs were injected into the load-bearing layer of rat abdominal walls prior to laparotomy, and cell viability was confirmed. Wound mechanical properties were measured over 28 days. The incidence and severity of laparotomy wound failure was measured in an incisional hernia model.
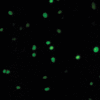
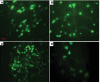
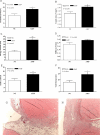
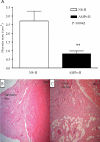
Results: AMP cells were viable in laparotomy wounds for at least 28 days and did not migrate to other tissues. Laparotomy wound-breaking strength was increased by postoperative day 7 following AMP therapy. AMP therapy reduced the incidence of hernia formation and the size of hernia defects. Histology suggested stimulated wound fibroplasia and angiogenesis.
Conclusions: AMP cell therapy reduces the incidence of laparotomy wound failure by accelerating the recovery of wound-breaking strength. This results in fewer incisional hernias and smaller hernia defects.
Figures
References
-
- Dubay DA, Franz MG. Acute wound healing: the biology of acute wound failure. Surg Clin N Am. 2003;83(3):463–481. - PubMed
-
- Robson MC, Mustoe TA, Hunt TK. The future of recombinant growth factors in wound healing. Am J Surg. 1998;176(suppl 2A):80–82. - PubMed
-
- Franz MG, Kuhn MA, Wright TE, Wachtel TL, Robson MC. Use of the wound healing trajectory as an outcome determinant for acute wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2000;8(6):511–516. - PubMed
-
- Franz MG, Kuhn MA, Nguyen K, et al. Transforming growth factor b2 lowers the incidence of incisional hernias. J Surg Res. 2001;97(2):109–116. - PubMed
-
- Robson MC, Steed DL, Franz MG. Wound healing: biologic features and approaches to maximize healing trajectories. Curr Probl Surg. 2001;38(2):64–140. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
