Expression analysis of the ligands for the Natural Killer cell receptors NKp30 and NKp44
- PMID: 18092004
- PMCID: PMC2129109
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001339
Expression analysis of the ligands for the Natural Killer cell receptors NKp30 and NKp44
Abstract
Background: The natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCR) are important to stimulate the activity of Natural Killer (NK) cells against transformed cells. Identification of NCR ligands and their level of expression on normal and neoplastic cells has important implications for the rational design of immunotherapy strategies for cancer.
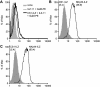
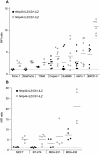
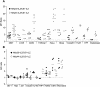
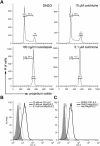
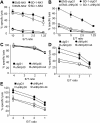
Methodology/principal findings: Here we analyze the expression of NKp30 ligand and NKp44 ligand on 30 transformed or non-transformed cell lines of different origin. We find intracellular and surface expression of these two ligands on almost all cell lines tested. Expression of NKp30 and NKp44 ligands was variable and did not correlate with the origin of the cell line. Expression of NKp30 and NKp44 ligand correlated with NKp30 and NKp44-mediated NK cell lysis of tumor cells, respectively. The surface expression of NKp30 ligand and NKp44 ligand was sensitive to trypsin treatment and was reduced in cells arrested in G(2)/M phase.
Conclusion/significance: These data demonstrate the ubiquitous expression of the ligands for NKp30 and NKp44 and give an important insight into the regulation of these ligands.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

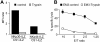
References
-
- Zamai L, Ponti C, Mirandola P, Gobbi G, Papa S, et al. NK cells and cancer. J Immunol. 2007;178:4011–4016. - PubMed
-
- Lee SH, Miyagi T, Biron CA. Keeping NK cells in highly regulated antiviral warfare. Trends Immunol. 2007;28:252–259. - PubMed
-
- Arnon TI, Markel G, Mandelboim O. Tumor and viral recognition by natural killer cells receptors. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:348–358. - PubMed
-
- Ljunggren HG, Malmberg KJ. Prospects for the use of NK cells in immunotherapy of human cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:329–339. - PubMed
-
- Hayakawa Y, Smyth MJ. Innate immune recognition and suppression of tumors. Adv Cancer Res. 2006;95:293–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

