Neurogenesis impairment and increased cell death reduce total neuron number in the hippocampal region of fetuses with Down syndrome
- PMID: 18093248
- PMCID: PMC8095525
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00113.x
Neurogenesis impairment and increased cell death reduce total neuron number in the hippocampal region of fetuses with Down syndrome
Abstract
We previously obtained evidence for reduced cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus (DG) of fetuses with Down syndrome (DS), suggesting that the hippocampal hypoplasia seen in adulthood may be caused by defective early neuron production. The goal of this study was to establish whether DS fetuses (17-21 weeks of gestation) exhibit reduction in total cell number in the DG, hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus (PHG). Volumes of the cellular layers and cell number were estimated with Cavalieri's principle and the optical fractionator method, respectively. We found that in DS fetuses all investigated structures had a reduced volume and cell number. Analysis of cell phenotype showed that DS fetuses had a higher percentage of cells with astrocytic phenotype but a smaller percentage of cells with neuronal phenotype. Immunohistochemistry for Ki-67, a marker of cycling cells, showed that DS fetuses had less proliferating cells in the germinal zones of the hippocampus and PHG. We additionally found that in the hippocampal region of DS fetuses there was a higher incidence of apoptotic cell death. Results show reduced neuron number in the DS hippocampal region and suggest that this defect is caused by disruption of neurogenesis and apoptosis, two fundamental processes underlying brain building.
Figures

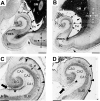
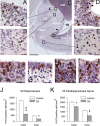
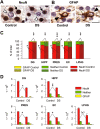
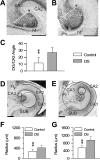
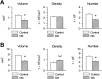
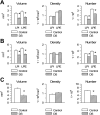

References
-
- Arnold SE, Trojanowski JQ (1996) Human fetal hippocampal development: I. Cytoarchitecture, myeloarchitecture, and neuronal morphologic features. J Comp Neurol 367:274–292. - PubMed
-
- Aylward EH, Habbak R, Warren AC, Pulsifer MB, Barta PE, Jerram M, Pearlson GD (1997) Cerebellar volume in adults with Down syndrome. Arch Neurol 54:209–212. - PubMed
-
- Aylward EH, Li Q, Honeycutt NA, Warren AC, Pulsifer MB, Barta PE et al (1999) MRI volumes of the hippocampus and amygdala in adults with Down's syndrome with and without dementia. Am J Psychiatry 156:564–568. - PubMed
-
- Bahn S, Mimmack M, Ryan M, Caldwell MA, Jauniaux E, Starkey M et al (2002) Neuronal target genes of the neuron‐restrictive silencer factor in neurospheres derived from fetuses with Down's syndrome: a gene expression study. Lancet 359:310–315. - PubMed
-
- Becker L, Mito T, Takashima S, Onodera K (1991) Growth and development of the brain in Down syndrome. Prog Clin Biol Res 373:133–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

