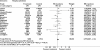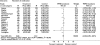Does pharmacist-led medication review help to reduce hospital admissions and deaths in older people? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 18093253
- PMCID: PMC2291244
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.03071.x
Does pharmacist-led medication review help to reduce hospital admissions and deaths in older people? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
We set out to determine the effects of pharmacist-led medication review in older people by means of a systematic review and meta-analysis covering 11 electronic databases. Randomized controlled trials in any setting, concerning older people (mean age > 60 years), were considered, aimed at optimizing drug regimens and improving patient outcomes. Our primary outcome was emergency hospital admission (all cause). Secondary outcomes were mortality and numbers of drugs prescribed. We also recorded data on drug knowledge, adherence and adverse drug reactions. We retrieved 32 studies which fitted the inclusion criteria. Meta-analysis of 17 trials revealed no significant effect on all-cause admission, relative risk (RR) of 0.99 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.87, 1.14, P = 0.92], with moderate heterogeneity (I(2) = 49.5, P = 0.01). Meta-analysis of mortality data from 22 trials found no significant benefit, with a RR of mortality of 0.96 (95% CI 0.82, 1.13, P = 0.62), with no heterogeneity (I(2) = 0%). Pharmacist-led medication review may slightly decrease numbers of drugs prescribed (weighted mean difference = -0.48, 95% CI -0.89, -0.07), but significant heterogeneity was found (I(2) = 85.9%, P < 0.001). Results for additional outcomes could not be pooled, but suggested that interventions could improve knowledge and adherence. Pharmacist-led medication review interventions do not have any effect on reducing mortality or hospital admission in older people, and can not be assumed to provide substantial clinical benefit. Such interventions may improve drug knowledge and adherence, but there are insufficient data to know whether quality of life is improved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pharmacist-led medication review: comment on Holland et al. 2008.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;66(4):575; author reply 576. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03226.x. Epub 2008 May 21. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18637889 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Begley S, Livingstone C, Hodges N, Williamson V. Impact of domiciliary pharmacy visits on medication management in an elderly population. Int J Pharm Pract. 1997;5:111–21.
-
- Stewart S, Pearson S, Horowitz JD. Effects of a home-based intervention among patients with congestive heart failure discharged from acute hospital care. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158:1067–72. - PubMed
-
- Kennie NR, Schuster BG, Einarson TR. Critical analysis of the pharmaceutical care research literature. Ann Pharmacother. 1998;32:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Beney J, Bero LA, Bond C. Expanding the roles of outpatient pharmacists: effects on health services utilisation, costs, and patient outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. CD000336. - PubMed
-
- Kaboli PJ, Hoth AB, McClimon BJ, Schnipper JL. Clinical pharmacists and inpatient medical care: a systematic review. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:955–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical