Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry peak sorting algorithm
- PMID: 18093607
- PMCID: PMC3933977
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.11.101
Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry peak sorting algorithm
Abstract
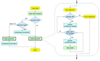
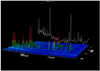
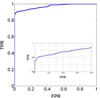
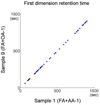
We report a novel peak sorting method for the two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC x GC/TOF-MS) system. The objective of peak sorting is to recognize peaks from the same metabolite occurring in different samples from thousands of peaks detected in the analytical procedure. The developed algorithm is based on the fact that the chromatographic peaks for a given analyte have similar retention times in all of the chromatograms. Raw instrument data are first processed by ChromaTOF (Leco) software to provide the peak tables. Our algorithm achieves peak sorting by utilizing the first- and second-dimension retention times in the peak tables and the mass spectra generated during the process of electron impact ionization. The algorithm searches the peak tables for the peaks generated by the same type of metabolite using several search criteria. Our software also includes options to eliminate non-target peaks from the sorting results, e.g., peaks of contaminants. The developed software package has been tested using a mixture of standard metabolites and another mixture of standard metabolites spiked into human serum. Manual validation demonstrates high accuracy of peak sorting with this algorithm.
Figures










References
-
- Harrigan GG, Goodacre R, editors. Metabolic Profiling: Its Role in Biomarker Discovery and Gene Function Analysis. Boston, MA: Kluwer; 2003. p. 171.
-
- Watkins SM, German JB. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2002;4:224. - PubMed
-
- Dunckley T, Coon KD, Stephan DA. Drug Discovery Today. 2005;10:326. - PubMed
-
- Harrigan GG, Goodacre R, editors. Metabolic Profiling: Its Role in Biomarker Discovery and Gene Function Analysis. Boston, MA: Kluwer; 2003. p. 199.
-
- Dunn WB, Ellis DI. Trends Anal. Chem. 2005;24:285.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

