Uric acid as a pathogenic factor in preeclampsia
- PMID: 18093648
- PMCID: PMC3319018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2007.11.001
Uric acid as a pathogenic factor in preeclampsia
Abstract
Hyperuricemia is a common finding in preeclamptic pregnancies evident from early pregnancy. Despite the fact that elevated uric acid often pre-dates the onset of clinical manifestations of preeclampsia, hyperuricemia is usually considered secondary to altered kidney function. Increased serum uric acid is associated with hypertension, renal disease and adverse cardiovascular events in the non-pregnant population and with adverse fetal outcomes in hypertensive pregnancies. We hypothesize that an elevated concentration of uric acid in preeclamptic women is not simply a marker of disease severity but rather contributes directly to the pathogenesis of the disorder. Using epidemiological and experimental evidence, gained largely outside of pregnancy, we will propose pathogenic roles for uric acid in preeclamptic pregnancies. Uric acid's ability to promote inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction will be highlighted with discussions of the potential impact on placental development and function and maternal vascular health.
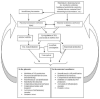
Figures
References
-
- Powers RW, Bodnar LM, Ness RB, Cooper KM, Gallaher MJ, Frank MP, Daftary AR, Roberts JM. Uric acid concentrations in early pregnancy among preeclamptic women with gestational hyperuricemia at delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194:160. - PubMed
-
- Johnson RJ, Kang DH, Feig D, Kivlighn S, Kanellis J, Watanabe S, Tuttle KR, Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Herrera-Acosta J, Mazzali M. Is there a pathogenetic role for uric acid in hypertension and cardiovascular and renal disease? Hypertension. 2003;41:1183–90. - PubMed
-
- Kang DH, Finch J, Nakagawa T, Karumanchi SA, Kanellis J, Granger J, Johnson RJ. Uric acid, endothelial dysfunction and pre-eclampsia: searching for a pathogenetic link. J Hypertens. 2004;22:229–35. - PubMed
-
- Parks DA, Williams TK, Beckman JS. Conversion of xanthine dehydrogenase to oxidase in ischemic rat intestine: a reevaluation. Am J Physiol. 1988;254:G768–74. - PubMed
-
- Tan S, Gelman S, Wheat JK, Parks DA. Circulating xanthine oxidase in human ischemia reperfusion. South Med J. 1995;88:479–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources