Therapeutic B cell depletion impairs adaptive and autoreactive CD4+ T cell activation in mice
- PMID: 18093919
- PMCID: PMC2409235
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0709205105
Therapeutic B cell depletion impairs adaptive and autoreactive CD4+ T cell activation in mice
Abstract
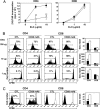
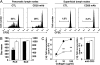
CD20 antibody depletion of B lymphocytes effectively ameliorates multiple T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases through mechanisms that remain unclear. To address this, a mouse CD20 antibody that depletes >95% of mature B cells in mice with otherwise intact immune systems was used to assess the role of B cells in CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell activation and expansion in vivo. B cell depletion had no direct effect on T cell subsets or the activation status of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells in naive mice. However, B cell depletion impaired CD4(+) T cell activation and clonal expansion in response to protein antigens and pathogen challenge, whereas CD8(+) T cell activation was not affected. In vivo dendritic cell ablation, along with CD20 immunotherapy, revealed that optimal antigen-specific CD4(+) T cell priming required both B cells and dendritic cells. Most importantly, B cell depletion inhibited antigen-specific CD4(+) T cell expansion in both collagen-induced arthritis and autoimmune diabetes mouse models. These results provide direct evidence that B cells contribute to T cell activation and expansion in vivo and offer insights into the mechanism of action for B cell depletion therapy in the treatment of autoimmunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: T.F.T. is a paid consultant for MedImmune, Inc. and a consultant and shareholder for Angelica Therapeutics, Inc. J.C.P is a paid consultant for Angelica Therapeutics, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Ermann J, Fathman CG. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:759–761. - PubMed
-
- Edwards JCW, Cambridge G. Rheumatology. 2001;40:205–211. - PubMed
-
- Stasi R, Del Poeta G, Stipa E, Evangelista ML, Trawinska MM, Cooper N, Amadori S. Blood. 2007;110:2924–2930. - PubMed
-
- Edwards JCW, Cambridge G. Rheumatology. 2005;44:151–156. - PubMed
-
- Lipsky PE. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:764–766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

