MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib
- PMID: 18093943
- PMCID: PMC2409244
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0710370104
MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib
Abstract
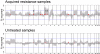
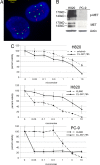
In human lung adenocarcinomas harboring EGFR mutations, a second-site point mutation that substitutes methionine for threonine at position 790 (T790M) is associated with approximately half of cases of acquired resistance to the EGFR kinase inhibitors, gefitinib and erlotinib. To identify other potential mechanisms that contribute to disease progression, we used array-based comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) to compare genomic profiles of EGFR mutant tumors from untreated patients with those from patients with acquired resistance. Among three loci demonstrating recurrent copy number alterations (CNAs) specific to the acquired resistance set, one contained the MET proto-oncogene. Collectively, analysis of tumor samples from multiple independent patient cohorts revealed that MET was amplified in tumors from 9 of 43 (21%) patients with acquired resistance but in only two tumors from 62 untreated patients (3%) (P = 0.007, Fisher's Exact test). Among 10 resistant tumors from the nine patients with MET amplification, 4 also harbored the EGFR(T790M) mutation. We also found that an existing EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma cell line, NCI-H820, harbors MET amplification in addition to a drug-sensitive EGFR mutation and the T790M change. Growth inhibition studies demonstrate that these cells are resistant to both erlotinib and an irreversible EGFR inhibitor (CL-387,785) but sensitive to a multikinase inhibitor (XL880) with potent activity against MET. Taken together, these data suggest that MET amplification occurs independently of EGFR(T790M) mutations and that MET may be a clinically relevant therapeutic target for some patients with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: V.M. and W.P. are part of a pending patent application on
Figures

References
-
- Pao W, Miller VA. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2556–2568. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et al. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Riely GJ, Politi KA, Miller VA, Pao W. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:7232–7241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

